Table of Contents
Introduction
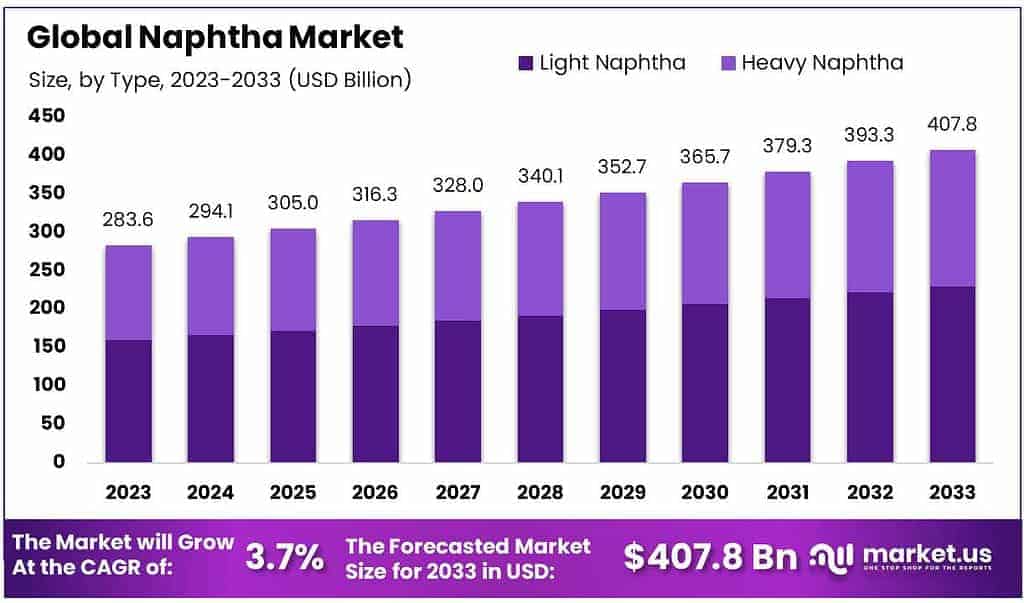
The global naphtha market is poised for significant growth, with its size expected to reach approximately USD 407.8 billion by 2033, up from USD 283.6 billion in 2023. This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.7% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033.
Naphtha, a crucial feedstock in the petrochemical industry, plays a vital role in the production of chemicals, plastics, and fuels. The increasing demand for petrochemical products, especially in emerging markets, is one of the primary drivers of market expansion.
Moreover, the growth of industries such as automotive, construction, and consumer goods is further fueling the demand for naphtha-based products. However, challenges such as fluctuating crude oil prices, environmental concerns, and regulatory pressures related to carbon emissions could impact market dynamics.
Recent developments show a rising focus on sustainable production practices, with key industry players investing in advanced technologies to reduce emissions and improve the efficiency of naphtha refining processes. The market is also seeing significant investments in new refining capacity in regions like Asia-Pacific, which is expected to remain the dominant market for naphtha.
While the global push for cleaner energy sources presents a challenge for traditional hydrocarbon-based products, naphtha’s versatility in various industrial applications continues to support its demand across sectors. The market’s growth prospects remain strong, driven by the ongoing need for high-quality petrochemical products and the expanding industrial base, although its trajectory will be influenced by both global energy trends and regulatory landscapes.
LG Chem has consistently focused on expanding its petrochemical production and refining capabilities, especially in naphtha, through strategic investments. The company has focused on improving its production efficiency and expanding its presence in the Asian market. They aim to secure a significant share of the global petrochemical market by enhancing their naphtha cracker capacities and integrating advanced technologies.
China Petrochemical (Sinopec) remains one of the world’s largest naphtha producers, leveraging its vast refining network and naphtha cracker facilities. The company has been investing heavily in expanding its naphtha refining capacity to meet growing domestic and global demand. Sinopec also focuses on improving product quality and reducing emissions in its refining processes.
Key Takeaways
- The global naphtha market is expected to reach a substantial worth of around USD 407.8 billion by 2033, indicating a significant growth trajectory from USD 283.6 billion in 2023. This growth, at a CAGR of 3.7%, is primarily attributed to the rising demand for transportation fuel globally.
- In 2023, Light Naphtha and Heavy Naphtha were the primary segments in the market, holding a strong position by securing over 56.5% of the market share.
- The main application segment for Naphtha was as a chemical feedstock. It accounted for over 63.8% of the total volume share in 2023.
- In 2023, Petrochemicals took the lead in the Naphtha market, holding a dominant position with over 51.6% market share.
- The Asia Pacific naphtha markets dominated global demand in 2023 and accounted for more than 58.4% of the total volume share.
Naphtha Statistics
Naphtha Feedstock and Market Trends
- The light naphtha analysis provides balances for light paraffinic/lean naphtha that is used as a feed for steam crackers and boils typically between 50°F (C5) and 160°F.
- The heavy naphtha analysis provides balances for heavy naphthenic/rich naphtha that is a good feed for heavy naphtha reformers and typically boils between 160°F and 370°F (C11).
- The European Agricultural Fund for Rural Development (EAFRD) counts on €95.5 billion to reinforce the EAGF measures by strengthening the social, environmental, and economic sustainability of rural areas.
- With a €291.1 billion budget, the European Agricultural Guarantee Fund (EAGF) provides financial assistance to rural development projects and to farmers, while also promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
- €21 billion will fund measures to support and stabilize agricultural markets, following the guidelines of the Common Market Organisation (CMO).
Naphtha Supply Agreements and Agricultural Funding
- €270 billion will be provided to farmers for income support schemes, including a basic payment scheme, a payment for sustainable farming methods, and a payment for young farmers, all subject to compliance with EU rules on food safety, environmental protection, and animal welfare.
- Haldia Petrochemicals Limited (HPL) has secured a long-term naphtha supply agreement with Qatar Energy. QatarEnergy. The agreement was signed through its subsidiary. The deal will provide up to 2 million tons of naphtha to HPL over the next decade starting from Q2 2024
- Naphtha used as the main feedstock for the petrochemical industry is classified into light naphtha, whose boiling point is 35~130°; heavy naphtha, whose boiling point is 130~220°; and full-range naphtha, containing both these two types of naphtha.
- The agreement, set to commence in April 2025, will see up to 18 million tonnes (mt) of naphtha delivered to Shell throughout the contract.
- QatarEnergy inked a long-term agreement to supply Japan’s Idemitsu Kosan Co. Ltd with up to 6 million tons of naphtha over the next 10 years starting in July 2024.
Emerging Trends
- Growing Demand in Petrochemical Industry: Naphtha is a key raw material used in the production of petrochemicals, especially in making plastics like polyethylene and polypropylene. As the global demand for plastics, synthetic rubber, and other chemicals increases, naphtha continues to be a critical feedstock for these industries.
- Shift Toward Cleaner Fuels: As the world moves towards reducing carbon emissions, there is a growing push to use naphtha as a cleaner alternative to heavier fuels like coal and oil. Naphtha is being used increasingly in refineries to produce gasoline and as a fuel in various industries thanks to its relatively cleaner-burning properties compared to heavier hydrocarbons.
- Naphtha as a Feedstock for Hydrogen Production: Naphtha is being looked at as an important feedstock for hydrogen production, especially through a process known as “reforming.” This is because naphtha contains hydrocarbons that can be converted into hydrogen. As hydrogen gains popularity as a clean energy source, naphtha’s role in producing “green hydrogen” is likely to grow, particularly in countries aiming for net-zero emissions.
- Price Volatility Linked to Crude Oil: Naphtha prices are closely tied to crude oil prices. This means that fluctuations in oil markets directly affect naphtha prices. The recent rise in oil prices and geopolitical factors have led to more price volatility, impacting the affordability and cost-effectiveness of using naphtha in various industries. For businesses relying on naphtha as a feedstock, this price volatility is becoming an important risk to manage.
- Rise of Bio-Naphtha: There is an emerging trend towards producing bio-naphtha, which is made from renewable sources like biomass or waste materials instead of crude oil. This bio-based version of naphtha is seen as a more sustainable alternative, helping reduce the carbon footprint of industries that use naphtha in chemical production or fuel blending.
Use Cases
- Petrochemical Production: Naphtha is a primary raw material used in the petrochemical industry to produce a variety of chemicals. These chemicals are the building blocks for many products we use every day, including plastics (like polyethylene and polypropylene), synthetic rubber, and fertilizers. It undergoes a process called “cracking” to break it down into smaller molecules that can be used to create these products.
- Fuel for Cars and Motor Vehicles: Naphtha is a key ingredient in the production of gasoline (petrol). Refineries often use it as a blending component to enhance the performance of the fuel. It helps increase the octane rating, which improves engine efficiency and reduces knocking (when fuel burns unevenly in an engine).
- The Solvent in Industrial Applications: Due to its solvent properties, naphtha is commonly used in cleaning agents and paint thinners. Its ability to dissolve oils, greases, and resins makes it useful in industries like automotive repair, painting, and chemical manufacturing. Naphtha-based solvents help to remove stubborn stains, clean equipment, and prepare surfaces for further treatment.
- Hydrogen Production: Naphtha is used as a feedstock in hydrogen production, particularly in a process called naphtha reforming. This involves heating naphtha in the presence of steam and a catalyst to produce hydrogen gas, which is used in various industries, including fuel production and refining.
- Fuel for Industrial Boilers and Power Plants: Naphtha is sometimes used as a fuel in industrial boilers and power plants, especially where there is a need for a cleaner alternative to coal or heavy oil. Its relatively high energy content makes it suitable for generating heat and electricity in power generation facilities.
Major Challenges
- Fluctuating Prices: Naphtha prices are directly impacted by the ups and downs of crude oil prices. When oil costs surge or drop unexpectedly, naphtha follows suit, leading to price instability. This creates significant challenges for industries that rely on naphtha, like petrochemicals and refineries.
- Environmental Concerns: As a byproduct of fossil fuels, naphtha contributes to environmental issues such as greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. While it is less polluting than some other fossil-based fuels like coal, burning naphtha still releases harmful emissions like carbon dioxide (CO2). This poses a challenge in the context of global climate goals and stricter environmental regulations, especially in industries like power generation and manufacturing.
- Reliance on Fossil Fuels: Naphtha’s production is intricately tied to crude oil refining, which is part of the larger global reliance on fossil fuels. As the world transitions toward renewable energy and seeks alternatives to oil-based products, the demand for naphtha could face long-term pressure. Renewable fuels like biofuels and hydrogen are becoming more competitive, which could diminish naphtha’s importance in the future.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Naphtha is primarily produced in large refining hubs located in key regions like the Middle East, Asia, and North America. Any disruption in these areas—such as geopolitical conflicts, natural disasters, or trade barriers—can create significant supply chain issues. These disruptions can cause shortages or price hikes, making it harder for businesses to secure a stable supply.
- Challenges in Refining: The process of converting crude oil into naphtha is intricate and requires specialized refining technology. The quality of the resulting naphtha can vary based on the type of crude oil used and the specific refining methods employed. This variability makes it challenging for refineries to maintain consistent product quality.
Market Growth Opportunities
- Expansion in Petrochemical Production: Naphtha is a key raw material in the production of petrochemicals, which are used to create a wide range of products, from plastics to synthetic fibers and rubber. As global demand for plastics and chemicals continues to rise—especially in emerging markets—there is an opportunity for increased use of naphtha in petrochemical plants.
- Shift Toward Bio-based Naphtha: With increasing environmental concerns and a push for sustainable energy, bio-naphtha—which is produced from renewable sources like biomass, waste oils, and plant-based materials—presents a promising growth opportunity. Bio-naphtha can be used as a cleaner alternative to fossil-based naphtha in both industrial applications and fuel production.
- Use in Hydrogen Production: Naphtha is increasingly being used as a feedstock for producing hydrogen, particularly through a process called naphtha reforming. Hydrogen is gaining attention as a clean energy source, especially in industries like transportation, power generation, and refining.
- Growing Demand for Cleaner Fuels: Naphtha is often used as a cleaner alternative to heavier fuels, like coal or diesel, in certain applications. As stricter environmental regulations are enforced globally, especially in areas like Europe and North America, naphtha is becoming more attractive as a low-sulfur fuel for industrial use.
- Naphtha as a Feedstock for Renewable Energy Solutions: Naphtha is used in various energy production processes, and with the growing focus on decarbonizing the energy sector, there is an opportunity to integrate naphtha into blended fuel solutions. For instance, it can be combined with biofuels or other renewable sources to create hybrid fuel products.
Key Players Analysis
- LG Chem is involved in the naphtha sector primarily for producing petrochemicals like ethylene and propylene. They use naphtha as a feedstock in their chemical manufacturing processes.
- China Petrochemical (Sinopec) is a key player in the naphtha sector, using naphtha as a feedstock in its refining and petrochemical operations to produce a range of chemicals and fuels.
- Chevron uses naphtha as a key raw material in its refining and petrochemical operations, producing gasoline, polymers, and other petrochemical products. The company focuses on efficient naphtha utilization for optimal product yields.
- Mangalore Refinery and Petrochemicals Limited (MRPL) in Naphtha Sector crude oil into high-quality naphtha, which is then used in petrochemical production, particularly for manufacturing plastics and synthetic materials.
- Reliance Industries is a major player in the naphtha sector, utilizing naphtha for its large petrochemical operations, particularly in the production of polymers, chemicals, and synthetic materials.
- Exxon Mobil Corporation processes naphtha in its refineries to produce gasoline and petrochemical feedstocks, which are essential for manufacturing plastics, chemicals, and synthetic materials. The company focuses on enhancing production efficiency and sustainability.
- BP processes naphtha in its refineries to produce high-value petrochemical products like plastics and solvents. The company focuses on improving efficiency and reducing carbon emissions in naphtha-based operations.
- Shell uses naphtha as a key feedstock in its petrochemical operations, producing a variety of chemicals, including ethylene and polyethylene. The company is committed to enhancing the sustainability of its naphtha processes.
- SABIC utilizes naphtha as a primary feedstock in its petrochemical plants, producing chemicals like ethylene, propylene, and other key polymers. The company focuses on innovation and sustainability in its naphtha-based operations.
- CNPC in Naphtha Sector: CNPC (China National Petroleum Corporation) uses naphtha as a key feedstock in refining and petrochemical production, including the creation of chemicals and plastics. The company is focused on optimizing production efficiency.
- China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (Sinopec) in Naphtha Sector: Sinopec processes naphtha to produce key petrochemical products like ethylene and polypropylene. The company plays a significant role in naphtha-based chemical production, aiming for sustainability and energy efficiency.
- Formosa Petrochemical Corporation in Naphtha Sector: Formosa Petrochemical uses naphtha as a key feedstock in its petrochemical plants, producing chemicals like ethylene, propylene, and polyethylene. The company focuses on maximizing production efficiency and sustainability.
- Saudi Aramco refines naphtha to produce valuable petrochemical products like ethylene and propylene. The company integrates naphtha-based production in its global energy strategy, aiming for both economic and environmental performance.
- Lotte Chemical utilizes naphtha in its petrochemical operations to produce key products such as ethylene and plastics. The company emphasizes innovative technologies to improve product yields and sustainability.
Conclusion
Naphtha remains a vital resource in industries like petrochemicals, energy, and transportation. While challenges like price volatility and environmental impact persist, opportunities for growth in cleaner fuels, bio-based naphtha, and hydrogen production offer the potential for its continued importance as the world transitions to more sustainable solutions.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





