Table of Contents
Introduction
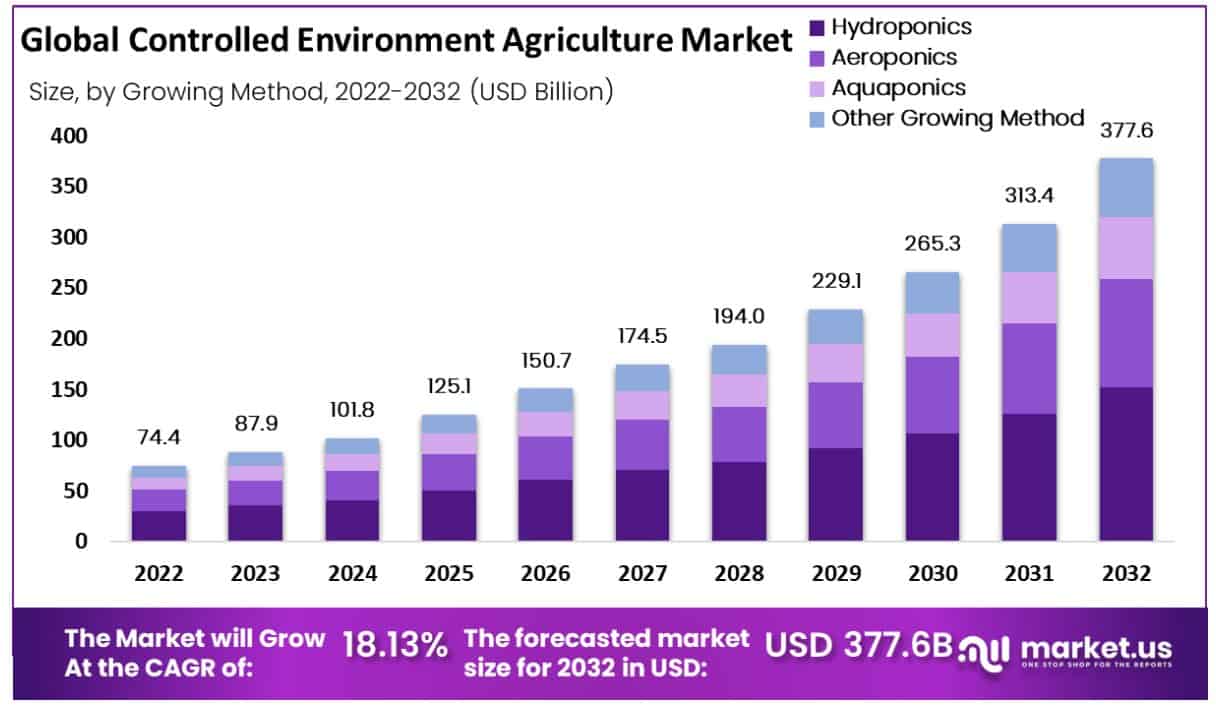
The Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) Market is poised for substantial growth, projected to expand from USD 87.9 billion in 2023 to USD 377.6 billion by 2033, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.13%. This surge is fueled by the escalating demand for fresh, healthy, and sustainably grown produce. CEA technologies, such as hydroponics, aquaponics, and aeroponics, support this growth by enabling year-round crop production under controlled conditions, significantly enhancing yield and quality while minimizing environmental impacts.
Challenges in the CEA market include high initial setup and operational costs, and the complexity of managing advanced agricultural technologies. Additionally, the market faces hurdles like the need for significant capital investment and the challenges associated with scaling operations.
Recent developments in the Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) market have highlighted significant growth and innovation across key players. Europe currently leads the market, with companies like SP ZO Co and Fresh Box innovating in CEA farming methods, contributing substantially to the region’s market share which stands at 27%. North America and Asia-Pacific are also noted for their significant growth potential due to increasing urbanization and population demands.
In terms of technology advancements, the focus has been extreme on hydroponics, which remains a dominant method in the CEA sector due to its efficiency in using resources like water and nutrients. This method, alongside others such as aeroponics and aquaponics, is becoming increasingly important as it allows for high yields without the extensive use of soil, which is becoming scarcer.
Financially, the industry is seeing substantial investments. The nutrients segment within the CEA market is particularly lucrative, driving much of the revenue growth expected to increase profitability by 20-25% in the coming years. Lighting technology also plays a crucial role, with advancements in LED technologies helping to reduce costs and improve efficiency, thereby supporting the growth of the lighting components market within CEA.
Overall, the Controlled Environment Agriculture market is set to transform how food is grown, offering solutions that align with global sustainability goals and the increasing consumer preference for locally-grown produce.
Controlled Environment Agriculture Statistics
- Market Growth (2022-2032): Global revenues of USD 87.9 billion in 2023, are expected to grow at a CAGR of 18.1% to exceed this figure by 2032.
- Crop Type Analysis: Tomatoes are the most lucrative crop, constituting 45% of market revenues in 2022.
- Regional Dominance: Europe led with a 27% market share in 2022, driven by innovative CEA solutions from companies like SP ZO Co and Fresh Box.
- Chester County, PA, contributes over $3 billion to the local economy through agriculture.
- Auburn University received a $9.95 million grant from the USDA for “Reimagining Controlled Environment in a Low-Carbon World” project.
- CEA is highly productive and efficient, conserving up to 95% of water compared to traditional farming methods.
- Compare CEA energy usage (6,173 to 19,676 kWh per tonne) with import environmental impact.
- Found CEA beneficial for climate mitigation in 4 cities.
- Ohio’s CEA contributes $124 billion to the state’s economy.
- Ohio boasts over 1,300 food manufacturers.
- The state hosts more than 14 CEA facilities.
- 80 Acres Farms, specializing in indoor farming, chose Ohio for its headquarters.
- UAg Vertical Farm on campus produces food year-round, 10 times more productive than outdoor gardens.
- Vertical Farming Benefits is Low water use (~80 to 90% reduction)
- On average, artificial lighting is used for 16 h/day in indoor agriculture
- Electrical energy costs for lighting can be 25 to 30% of operational costs
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) highlight a significant shift towards more technologically advanced and sustainable practices in the agricultural sector. Key developments focus on optimizing growing conditions and maximizing crop yields through the integration of cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors. These innovations are crucial for improving efficiency and reducing the ecological footprint of farming practices.
The industry is increasingly adopting vertical farming, aquaponics, and hydroponics, leveraging automation to enhance productivity and sustainability. Despite these advances, the sector faces economic challenges, such as high initial setup costs and ongoing operational expenses, which can be barriers to entry and expansion. Companies are exploring ways to make CEA more energy-efficient and cost-effective, particularly through the use of renewable energy sources.
Moreover, the geographical focus of CEA innovations is shifting. Regions with limited arable land, such as the Middle East, are emerging as new hubs for CEA development, driven by government support and incentives. This regional variation underscores the adaptability of CEA technologies to different economic and environmental conditions.
Overall, while the potential for CEA to revolutionize food production is vast, realizing this potential requires overcoming significant technological and economic hurdles. The focus for future developments in the sector is likely to revolve around improving the affordability and accessibility of these technologies, making them more viable for broader adoption.
Use Cases
- Optimizing Crop Growth: CEA systems are pivotal in enhancing plant growth by controlling environmental factors such as light, temperature, and humidity. Innovative technologies like hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics are employed within these controlled settings to maximize crop yield and quality without reliance on soil. This method is particularly effective for producing high-demand crops like leafy greens, tomatoes, and herbs.
- Sustainable Production Methods: CEA offers sustainable solutions by significantly reducing the need for water and pesticides compared to traditional farming. For example, advanced greenhouses and vertical farms use up to 95% less water than open-field agriculture. This approach not only conserves essential resources but also supports sustainable agricultural practices, even in regions with limited arable land or adverse climatic conditions.
- Year-Round Farming: The controlled conditions in CEA facilities allow for year-round crop production, irrespective of seasonal changes. This can be particularly beneficial in colder climates where traditional farming yields are limited to specific months. CEA provides a stable, predictable supply of fresh produce throughout the year.
- Localizing Food Production: With CEA, food production can be localized, reducing the need for long transportation distances. This not only ensures fresher produce for consumers but also reduces carbon emissions associated with transportation. Localized production is increasingly valued in urban centers, where space is limited and demand for fresh produce is high.
- Research and Development: CEA is also a valuable tool for agricultural research and development. By controlling environmental variables, researchers can experiment with plant genetics, growth patterns, and agricultural inputs more effectively. This contributes to advancements in crop science and the development of new agricultural technologies.
Key Players Analysis
AeroFarms is a pioneer in the Controlled Environment Agriculture sector, focusing on sustainability and innovative aeroponic technology. Based in Newark, New Jersey, AeroFarms optimizes growth conditions in their indoor vertical farms to produce crops with minimal water usage and no pesticides. Their technology allows for year-round production, maintaining high standards of food safety and quality. AeroFarms emphasizes environmental responsibility, demonstrated by its certification as a B Corporation, and aims to influence positive changes in agricultural practices through partnerships with major retailers like Amazon Fresh.
Gotham Greens operates urban greenhouses in cities across the United States to grow produce close to consumers, reducing food miles and ensuring freshness. They focus on using renewable energy sources and recycled water to cultivate their crops, emphasizing sustainability in every aspect of their operations. By controlling every factor of the growing environment, Gotham Greens ensures that their leafy greens and herbs are available year-round, regardless of external weather conditions, making them a significant player in urban agriculture and a model for sustainable food production practices.
Plenty is a key player in the Controlled Environment Agriculture sector, focusing on the sustainable production of greens and herbs through indoor vertical farming. With operations that utilize 95% less water than traditional farming, Plenty is expanding its technology to include a wide variety of crops. Their facilities in South San Francisco and upcoming ones in Compton, California, emphasize their ability to produce the equivalent yield of hundreds of acres of traditional farmland within a single indoor facility. This innovative approach not only enhances the quality and consistency of the produce but also significantly reduces the environmental impact, aligning with rising consumer demand for sustainable and locally sourced foods.
Lufa Farms, on the other hand, is renowned for pioneering rooftop farming in urban centers. Their farms are strategically located on building rooftops in Montreal, Canada, which enables direct delivery of fresh produce to consumers within the same cities. Lufa Farms focuses on growing a wide range of produce, from vegetables to herbs, emphasizing organic growing methods without the use of synthetic pesticides. This method of urban agriculture not only reduces transportation costs and emissions but also contributes to local food security and sustainability.
IDEA Protected Horticulture operates within the Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) sector, focusing on optimizing growing conditions in protective environments such as greenhouses. They specialize in engineering and consultancy to enhance the efficiency and productivity of horticultural projects, ensuring that plant growth is maximized through the careful management of resources like light, water, and nutrients. This strategic approach helps mitigate the risks associated with traditional farming and promotes sustainability.
Green Sense Farms is a pioneer in the vertical farming industry, utilizing advanced LED lighting and climate-controlled systems to grow a variety of leafy greens and herbs. Their operations are based in facilities that convert abandoned industrial spaces into productive agricultural sites, enabling year-round farming. This method significantly reduces water usage and eliminates the need for pesticides. Green Sense Farms also focuses on educational initiatives, offering training programs that prepare students for careers in the agricultural technology sector, further emphasizing their commitment to innovation and community engagement.
Metro Farms operates within the Controlled Environment Agriculture sector, focusing on sustainable practices to grow a variety of crops using advanced hydroponic systems in an urban setting. Their approach emphasizes the reduction of water use and the elimination of agricultural runoff, supporting a greener approach to urban agriculture. The farm is designed to provide fresh produce to city dwellers, minimizing the carbon footprint associated with transportation and offering a resilient food source for urban communities.
Mirai, known for operating one of the world’s largest indoor farm facilities in Japan, is a prominent player in the Controlled Environment Agriculture sector. Their facility uses stacked layers in a controlled environment to maximize space efficiency and crop output. Mirai’s use of advanced technologies in lighting and environmental control systems enables them to produce crops with reduced water and energy usage. The company focuses on sustainable practices and consistent crop production, aiming to contribute to food security and reduce environmental impacts.
Sky Greens is renowned for its innovative approach to vertical farming, utilizing a patented low-carbon, hydraulic-driven system that maximizes space and resource efficiency. Their technology enables the cultivation of vegetables in rotating tiers, allowing for uniform exposure to sunlight, irrigation, and nutrients, which significantly boosts yield per unit area. This system is particularly beneficial in urban settings like Singapore, where land is scarce. Sky Greens focuses on sustainability, using natural sunlight and a water-recycling system to minimize energy and water usage, enhancing food security and safety while maintaining the high quality and taste of the produce.
Greenland’s work in Controlled Environment Agriculture is less documented in the context of the leading sources available, which focus primarily on more prominent players in the industry. For specific information on Greenland within the CEA sector, direct industry sources or company releases would be more informative.
Scafil does not appear to have a visible presence or specific information available in the context of Controlled Environment Agriculture based on the current data from the web. They might not be significantly involved or mentioned in the CEA sector discussions or documentation available online.
Jingpeng operates one of China’s largest indoor farming facilities, specializing in soilless agriculture using liquid solutions and LED lighting to grow vegetables like lettuce and cabbage. This innovative approach allows for energy savings and higher control over agricultural conditions, making it a prominent example of modern CEA practices in an urban setting.
Metropolis Farms is an innovator in the Controlled Environment Agriculture sector, particularly noted for its advancements in indoor agricultural lighting technology. Their development, the OneBallast system, significantly reduces energy consumption by allowing a 315-watt bulb to operate at just 110 watts. This breakthrough not only decreases energy use by over 60% but also reduces the heat generated, thus lessening the need for ambient temperature control. This technology is poised to enhance the economics of indoor farming, particularly for commercially grown flowering plants.
Garden Fresh Farms is another notable player in the Controlled Environment Agriculture industry. However, specific details about their current operations, technology, or business model were not highlighted in the latest available sources. For detailed, up-to-date information, direct inquiries to the company or industry-specific publications would be more informative.
Infinite Harvest is a prominent player in the Controlled Environment Agriculture sector, operating an advanced vertical farm near Denver, Colorado. This facility specializes in growing a variety of fresh and local greens, delivering them to supermarkets within 24 to 48 hours of harvest to ensure peak freshness. Infinite Harvest’s farming technology is highly sustainable, utilizing 90% less water than traditional farming methods and achieving significant yield increases per acre. By using non-GMO seeds and avoiding harmful chemicals, their produce is environmentally friendly. Additionally, their vertical farming setup allows for year-round production without the risks associated with adverse weather, pests, or diseases.
Conclusion
Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) represents a transformative approach in modern agriculture, addressing both the increasing global food demand and the challenges posed by climate change. By utilizing technologies such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and advanced greenhouse systems, CEA enables the production of crops year-round in a controlled setting, minimizing the use of water and pesticides and reducing the dependency on arable land.
As the technology evolves, it continues to expand its crop variety beyond leafy greens and herbs to more resource-intensive crops like tomatoes and strawberries, demonstrating its potential to significantly impact food supply chains. Furthermore, the adaptability of CEA to urban settings offers a promising solution to reduce food miles and ensure fresh produce availability in metropolitan areas, making it a cornerstone in the future of sustainable agriculture.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





