Table of Contents
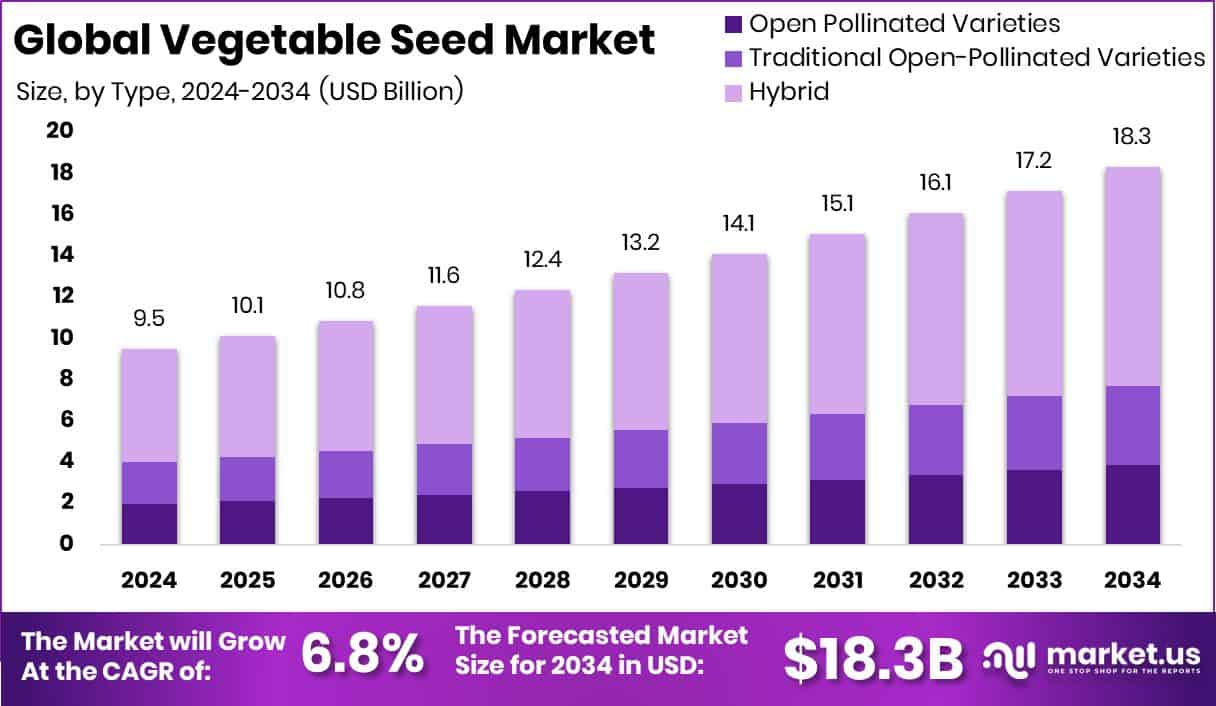
New York, NY – July 29, 2025 – The Global Vegetable Seed Market is expected to be worth around USD 18.3 billion by 2034, up from USD 9.5 billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2025 to 2034.
The vegetable seed market in India is supported by a growing national emphasis on horticulture and seed innovation. As of July 2025, India cultivates vegetables on approximately 27 million hectares, with productivity having increased from 10 t/ha to 18.5 t/ha over the past four decades.
Government measures have been substantive. In the fiscal year 2025–26, agricultural funding rose by more than 15 percent, reaching around ₹1.75 trillion (≈ USD 20 billion), with increasing allocations specifically directed toward high‑yield seed development and horticultural crop support.
At a national conference in July 2025, government representatives projected that India’s vegetable seed industry could expand from about USD 740 million in 2023–24 to approximately USD 970 million by 2030, assuming policy reforms and infrastructure investments are implemented effectively. Enhanced regulatory frameworks, digitized seed licensing platforms (such as SATHI), and investments in seed testing and processing facilities were highlighted as key enablers of this trajectory.
In addition, the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) facilitated a technology-transfer agreement in July 2025 for the advanced okra variety ‘Kashi Sahishnu’ (VRO‑111), which promises 20–23 percent higher farmer incomes along with reduced pesticide usage; this initiative exemplifies government‑supported public‑private collaboration in seed R&D.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Vegetable Seed Market is expected to be worth around USD 18.3 billion by 2034, up from USD 9.5 billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2025 to 2034.
- In 2024, Hybrid seeds led with a 58.4% share, favored for their high productivity and consistency.
- Conventional traits dominated the market, capturing 71.3% share due to reliability and widespread farmer preference.
- Inorganic seed form held a strong 78.4% share, driven by affordability and broad-scale cultivation practices.
- Solanaceae crops, including tomatoes and peppers, led with a 36.7% share due to global dietary demand.
- The Asia-Pacific market reached a total value of USD 4.5 billion in 2024.
Explore a sample copy of this report to preview key insights and strategic market highlights: https://market.us/report/vegetable-seed-market/request-sample/
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2024) | USD 9.5 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 18.3 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 6.8% |
| Segments Covered | By Type (Open Pollinated Varieties, Traditional Open-Pollinated Varieties, Hybrid), By Traits (Genetically Modified, Conventional), By Form (Organic, Inorganic), By Crop Type (Solanaceae, Root and Bulb, Cucurbit, Brassica, Leafy, Others) |
| Competitive Landscape | American Takii Inc., BASF SE, Bayer AG, Bejo Zaden B.V., East-West Seed Group, Enza Zaden BV, Groupe Limagrain Holding, Namdhari Seeds Pvt Ltd., Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel B.V., Sakata Seed Corporation, Syngenta Crop Protection AG, Takii & Co., Ltd., UPL Limited |
➤ Directly purchase a copy of the report— https://market.us/purchase-report/?report_id=153674
Key Market Segments
By Type Analysis
In 2024, hybrid seeds led the vegetable seed market with a 58.4% share, driven by their high yield, strong disease resistance, and adaptability to different climates. These traits make them a top choice for commercial growers aiming for consistent quality and productivity. Their uniform size and maturity also suit modern retail and large-scale operations.
As sustainable farming practices gain traction, hybrid seeds are increasingly favored for helping farmers reduce input costs while maximizing output. Awareness campaigns, farmer training, and field demonstrations have further boosted their adoption. With rising demand for vegetables due to growing populations and plant-based diets, hybrid seeds are expected to retain their lead, supported by their efficiency and alignment with modern agricultural needs.
By Traits Analysis
In 2024, conventional seeds accounted for 71.3% of the Vegetable Seed Market by traits, underscoring their stronghold due to long-standing trust in traditional breeding and open-pollinated varieties. These seeds remain popular among small to mid-sized farmers, especially in less mechanized regions, where seed saving and cost-effectiveness are key priorities.
Their consistent performance under local conditions and affordability contribute to their widespread use. Additionally, growing interest in non-GMO and chemical-free produce has further boosted the appeal of conventional seeds, as they align well with organic and sustainable farming goals. With rising emphasis on ecological balance and reduced reliance on synthetic inputs, conventional seeds continue to hold firm ground in the vegetable cultivation landscape.
By Form Analysis
In 2024, inorganic seeds dominated the Vegetable Seed Market by form, accounting for 78.4% of the segment. Their strong position stems from widespread use in commercial farming, where chemically treated seeds are valued for extended shelf life, quick germination, and early-stage pest resistance.
These seeds are often coated with protective agents like fungicides and nutrients, making them ideal for intensive agriculture and mechanized sowing. Their reliability, availability, and cost-efficiency have made them a preferred choice for large-scale producers aiming for consistent output. As global vegetable demand grows and farmers prioritize reduced crop losses, inorganic seeds continue to lead the market, aligned with productivity-focused and input-controlled farming systems.
By Crop Type Analysis
In 2024, Solanaceae crops led the Vegetable Seed Market by crop type, capturing a 36.7% share. This leadership is driven by the high consumption of tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants—key vegetables in global diets and widely used in both fresh and processed forms.
Their strong market presence is supported by their versatility across diverse climates and cultivation methods, from open fields to greenhouses. These crops offer attractive returns, prompting farmers to prioritize their production. Continuous breeding improvements have enhanced their yield, resilience, and shelf life, making them well-suited for evolving agricultural systems.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, Asia-Pacific led the global vegetable seed market with 47.9% of the share, valued at USD 4.5 billion. This dominance is attributed to the region’s vast agricultural activity, favorable growing conditions, and high vegetable consumption in countries like China, India, and across Southeast Asia. Rising populations and greater focus on high-yield, disease-resistant seeds have further strengthened demand.
North America and Europe continued to show steady performance, supported by advanced seed technologies and established farming systems. In Latin America, growth is emerging with increasing cultivation areas and a focus on export markets. Meanwhile, the Middle East & Africa, though holding a smaller portion, show promising potential due to food security initiatives.
Top Use Cases
- Yield and disease‑resistant hybrid cultivation: Hybrid vegetable seeds are widely utilized to drive higher productivity from limited land, offering faster maturity, uniform quality, and resistance to common diseases. These qualities support optimized farm outputs and reduce crop losses in commercial settings.
- Resource-efficient low-input farming: Utilization of high‑quality seeds allows farmers to use water, nutrients, and labor more judiciously, reducing waste while maintaining yields. Integrated farming strategies demonstrate that improved seed quality can lower environmental impact and boost returns per hectare.
- Food and nutrition security improvement: High‑performance vegetable seeds enhance rural nutrition by increasing the availability of nutrient‑dense produce. Seed distribution, along with farmer training, promotes food security and elevates livelihoods in underserved agricultural communities
Recent Developments
- In July 2024, Takii introduced a refreshed brand identity for its Sahin portfolio, which includes non‑GMO open‑pollinated vegetable and flower seeds. The rebranding strengthens the appeal to home gardeners and specialty growers, underlining quality and market relevance.
- In June 2024, BASF | Nunhems broadened its partnership with TS&L Seed Company. TS&L began distributing Nunhems® spinach, lettuce, watermelon, and melon seeds across California, Arizona, and Nevada. This expansion enhances access to BASF’s vegetable seed genetics for growers in these regions.
- In May 2024, Bayer teamed up with South Korean biotech firm G+FLAS to develop genome-edited tomato varieties enriched with vitamin D₃. This initiative aims to enhance the nutritional value of vegetables for wider dietary benefi.
Conclusion
The vegetable seed market continues to play a vital role in advancing global food security, sustainable farming, and economic resilience. With growing demand for nutritious produce and improved cultivation practices, quality seeds—both hybrid and conventional—remain central to agricultural productivity. Their role in enhancing yields, supporting climate resilience, and empowering smallholders underscores their enduring importance in modern food systems.




