Table of Contents
Overview
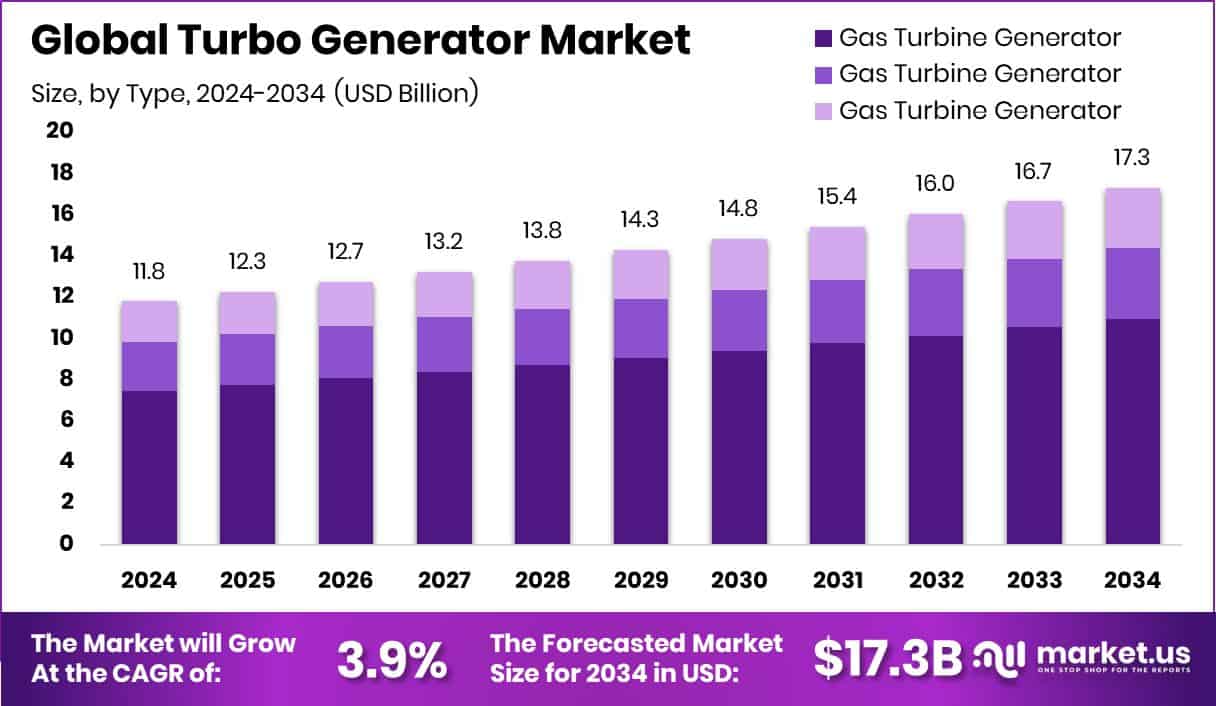
New York, NY – December 08, 2025 – The Turbo Generator Market is projected to expand steadily, rising from USD 11.8 billion in 2024 to nearly USD 17.3 billion by 2034, supported by a 3.9% CAGR between 2025 and 2034. Asia-Pacific leads global demand, holding a 45.1% share valued at USD 5.3 billion, driven by rapid capacity additions and grid modernization across major economies.
A turbo generator combines a turbine—powered by steam, gas, water, or nuclear heat—with an electrical generator to produce continuous, high-speed electricity. These systems are core to large-scale power plants, valued for their high efficiency, operational stability, and long service life. As a result, they remain central to thermal, nuclear, hydro, and newer clean-energy facilities.
Growth is strongly underpinned by public and private investments. GE Gas Power received USD 4.2 million to enhance gas turbine efficiency, while the U.S. Department of Energy committed USD 28 million toward ultrahigh-temperature gas turbine materials and USD 35 million for hydrokinetic turbine development.
Grid reliability needs are also shaping demand. First National Capital financed USD 148 million for natural-gas turbine generators, and Texas approved projects under a USD 7.2 billion loan program focused on strengthening gas-fired power capacity.
Opportunities are accelerating in advanced nuclear and hydro solutions. GE Steam Power and BHEL finalized a USD 165 million nuclear turbine contract, X-energy raised USD 700 million to scale nuclear energy, and Natel Energy secured USD 20 million to deploy restoration-focused hydro turbines.
➤ Click the sample report link for complete industry insights: https://market.us/report/global-turbo-generator-market/request-sample/
Key Takeaways
- The Global Turbo Generator Market is expected to be worth around USD 17.3 billion by 2034, up from USD 11.8 billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 3.9% from 2025 to 2034.
- Gas turbine generators lead the Turbo Generator Market with 63.3%, driven by efficiency, fast startup, and cleaner power generation.
- Air cooled systems hold 56.6% share due to lower water use, simpler design, and reduced maintenance needs.
- Coal power accounts for 44.9%, supported by existing plants requiring reliable turbo generators for baseload electricity.
- Asia-Pacific records 45.1% market share as the Turbo Generator Market totals USD 5.3 Bn.
➤ Directly purchase a copy of the report – https://market.us/purchase-report/?report_id=168018
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2024) | USD 11.8 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 17.3 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 3.9% |
| Segments Covered | By Type (Gas Turbine Generator, Steam Turbine Generator, Water Turbine Generator), By Cooling System (Air Cooled, Water Cooled, Hydrogen Cooled), By End-Use (Coal Power, Plants Nuclear Power Plants, Gas Power Plants, Others) |
| Competitive Landscape | EBARA CORPORATION, Siemens AG, Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited, Suzlon Energy Limited, ANSALDO ENERGIA, GE Vernova, TOSHIBA CORPORATION, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd., Andritz AG, Beijing BEIZHONG Steam |
Key Market Segments
By Type Analysis
In 2024, Gas Turbine Generators dominated the By Type segment of the Turbo Generator Market, accounting for a 63.3% market share. This strong position highlights the growing shift toward gas-based power generation, mainly because of its fast start-up capability and high operational flexibility.
Power utilities and industrial facilities continue to adopt gas turbine generators to handle peak electricity loads and stabilize grids affected by fluctuating renewable energy output. Their compact footprint and ability to produce high power output make them suitable for both large utility-scale plants and in-house captive power installations.
Another key advantage is the shorter installation and commissioning period when compared with alternative turbo generator technologies, enabling faster capacity expansion. Well-developed gas supply infrastructure, along with steady improvements in turbine efficiency and emissions control, further supports adoption.
As electricity demand grows across both developed and emerging economies, gas turbine generators remain critical for ensuring grid reliability and flexible power generation while maintaining their 63.3% market leadership.
By Cooling System Analysis
In 2024, air-cooled turbo generators led the By Cooling System segment of the Turbo Generator Market, holding a 56.6% share. Their dominance is mainly linked to a simpler system design that lowers maintenance needs and reduces operational complexity when compared with liquid-cooled alternatives.
Power producers increasingly choose air-cooled units because they do not require water circulation, treatment systems, or cooling towers. This makes them especially attractive in areas facing water scarcity. By removing water-related infrastructure, these generators also shorten installation timelines and help control overall project costs, enabling quicker plant commissioning.
Advances in airflow engineering and heat dissipation have improved thermal efficiency and system reliability, allowing air-cooled turbo generators to operate smoothly under constant load conditions. As utilities and industrial operators prioritize cost efficiency, ease of operation, and dependable performance, air-cooled systems continue to see strong adoption while maintaining their 56.6% market position.
By End-Use Analysis
In 2024, coal power remained the leading end-use segment in the turbo generator market, capturing a 44.9% share. This leadership highlights the ongoing dependence on coal-based generation to deliver stable, large-scale electricity, especially in regions with well-developed coal infrastructure.
Coal-fired power plants primarily operate as baseload facilities, creating steady demand for turbo generators capable of providing continuous and reliable output over extended operating periods. The long service life of these plants sustains requirements for turbo generators not only in new capacity additions but also in modernization and life-extension projects.
Ongoing investments in efficiency enhancements and operational reliability upgrades further support demand for robust turbo generator systems within existing coal assets. Despite gradual shifts toward cleaner energy sources, coal power continues to play a meaningful role in meeting electricity needs, allowing it to retain a 44.9% share in the turbo generator market’s end-use landscape.
Regional Analysis
The Turbo Generator Market demonstrates strong regional differences shaped by power demand, infrastructure development, and energy priorities. Asia-Pacific leads global adoption, holding a 45.1% share valued at USD 5.3 billion. This dominance is driven by rising electricity consumption, fast industrial expansion, and sustained investment across thermal, hydro, and nuclear power projects. Rapid urban growth and ongoing grid expansion in developing economies further strengthen demand for high-capacity, dependable turbo generators.
In North America, market activity is largely supported by replacement demand and efficiency-focused upgrades of existing power plants. Utilities emphasize grid reliability, stable output, and performance improvements, maintaining steady demand for modern turbo generator systems.
Europe represents a stable, technology-focused market where demand is linked to refurbishment and efficiency enhancement of aging power infrastructure rather than major new installations.
The Middle East & Africa show targeted demand tied to large utility projects and industrial power needs, supported by long-term energy development plans.
Latin America records moderate growth, driven by incremental grid expansion and the continued importance of conventional power generation.
Top Use Cases
- Large-scale electricity production (steam or gas power plants): Turbo generators are widely used in major power plants, where a steam or gas turbine spins the generator shaft to produce electricity for the grid.
- Hydropower electricity generation: When water flows through a turbine (e.g. from a dam or reservoir), the turbine drives a turbo generator — converting water’s kinetic or potential energy into electrical energy for supply.
- Combined-cycle power plants for higher efficiency: In some gas-turbine setups, exhaust heat from the turbine is used to produce steam, which then drives a steam turbine connected to a turbo generator — boosting overall efficiency compared to simple-cycle plants.
- Standby or peaking power for variable demand: Turbo generators driven by gas or small turbines can act as standby or peaking plants — powering up quickly when electricity demand spikes or when other plants go offline, ensuring grid stability.
- Captive power for industrial or remote facilities: Factories, hospitals, or remote installations may use on-site turbo-generator units (especially gas-turbine ones) to generate their own electricity — helpful where grid supply is unreliable or unavailable.
- Power for ships or special-purpose installations: Turbo generators also serve in marine or mobile applications (e.g. steam-turbo-electric ships), where turbines drive generators to provide electrical power and propulsion — useful in settings without external grid access.
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, EBARA announced successful operational testing of its electric turbo pump for rocket engines, using actual liquid propellants (LNG and liquid oxygen). The pump, developed since 2022, ran stably without leaks or abnormal vibrations. This is a big step in EBARA’s space-business push, aiming to simplify rocket fuel supply systems and enable reliable, efficient space launches.
- In December 2024, Siemens Energy and SSE launched a partnership named “Mission H2 Power” to develop gas turbine technology capable of running on 100% hydrogen while retaining the flexibility to operate on natural gas or a blend. This is meant to decarbonize gas-fired power plants, such as SSE’s Keadby 2 plant in the UK, using Siemens’ turbine tech.
Conclusion
The turbo generator market plays a vital role in supporting reliable and continuous power generation across utility and industrial applications. These systems remain essential for large power plants due to their high efficiency, stable performance, and long operating life.
Ongoing upgrades to existing facilities, along with the need for dependable baseload and flexible power, continue to support demand. Technological improvements in efficiency, cooling, and operational control are enhancing performance while reducing maintenance challenges.
As energy systems adjust to changing grid requirements and diverse fuel sources, turbo generators remain a core component of power infrastructure, helping utilities and industries deliver stable electricity while strengthening overall grid resilience.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





