Table of Contents
Introduction
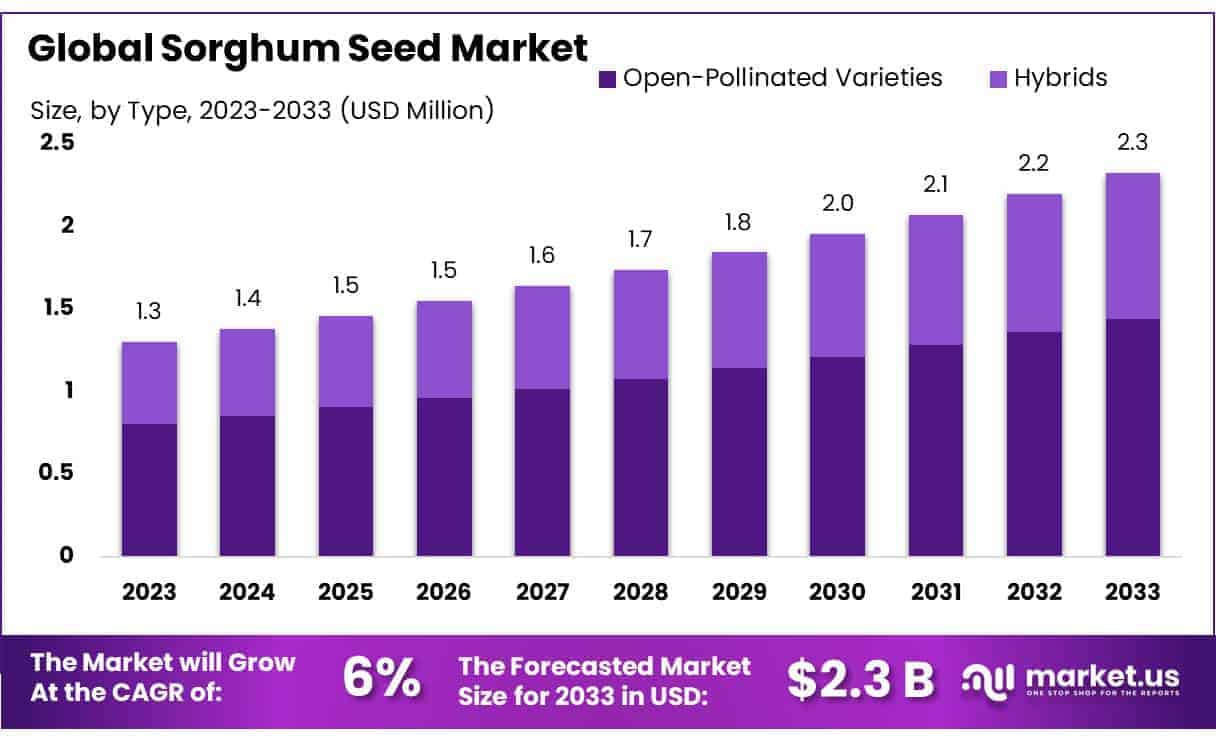
The Global Sorghum Seed Market is poised for substantial growth, projected to expand from USD 1.3 billion in 2023 to approximately USD 2.3 billion by 2033, achieving a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.0% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
This market’s growth can be attributed to the increasing demand for sorghum as a versatile crop used in food, fodder, and biofuel production, highlighting its rising popularity. Factors driving this demand include sorghum’s resilience to drought and heat, making it an attractive option for farmers in arid regions.
Additionally, the market is witnessing opportunities through technological advancements in seed breeding and genetics, which enhance yield and crop quality. The expansion of the sorghum seed market is further supported by a growing inclination towards gluten-free diets, for which sorghum is a preferred grain, thereby broadening its consumer base and application spectrum in various industries.
Moreover, the global trend toward sustainable agriculture boosts the sorghum seed market, as sorghum requires fewer resources than other grains, making it an eco-friendly choice. The market is also benefitting from increasing government support in various countries, encouraging sorghum cultivation through subsidies and research funding.
These elements collectively contribute to the broadening appeal and application of sorghum seeds, enhancing market opportunities and driving expansion across diverse geographical regions. As consumer awareness about the health benefits of sorghum increases, and as agricultural technologies continue to advance, the sorghum seed market is expected to maintain its upward trajectory, meeting the needs of a growing global population while supporting sustainable farming practices.
Key Takeaways
- Sorghum Seed Market size is expected to be worth around USD 2.3 Bn by 2033, from USD 1.3 Bn in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 6.0%.
- Hybrids held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 62.3% share in the sorghum seed market.
- Grain Sorghum held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.2% share.
- Grain Gram Flour held a dominant market position, capturing more than an 18.5% share.
- Animal Feed held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.1% share.
- North America dominated the global sorghum seed market, capturing a significant share of 43.3%
Sorghum Seed Statistics
Sorghum Seed Planting Techniques
- Most cultivars are annuals although some are perennial. Sorghum stems may reach over 4 m in height, with small grains of 3–4 mm in diameter.
- Although it is mostly self-pollinating, protogyny may cause at least 5% natural cross-pollination. The genetic integrity of sorghum accessions is thus maintained by selfing.
- Soil pH should be 5.5–8.5 and the plant will tolerate some salinity, alkalinity, and poor drainage.
- Level the field and make ridges 75 cm apart. This facilitates better establishment of seedlings and plant stands.
- Mark rows 75 cm apart across each tier, perpendicular to the length of the field, giving rows 3–9 m long, depending on the width of the plot.
Sorghum Seed Growth and Cultivation
- For field growth, prepare broad beds 1.5 m wide and 6 m long. For growing in a glasshouse, use pots of 30 cm diameter filled with a mixture of 3 parts black soil: 2 sand: and 1 farmyard manure.
- Germinate the wild species in paper cups and transplant them at 20 cm spacing in the field or in pots in the glasshouse.
- Sorghums grown for grain vary greatly in height, ranging from about 1 to 3 m.
- While 60% of wheat, barley, and corn in Europe are destined for animal feed, sorghum plays a complementary role.
- Five seed firms, who process over 96% of the sorghum seed in the U.S., provided information on seed clean-out rates and disposal methods of aspirated grain dust.
U.S. Sorghum Seed Production Insights
- Quantities of aspirated grain dust removed from sorghum planting seed ranged from 0.5% to less than 1%.
- Using the highest rate of dust collection (0.75%) and largest volume of sorghum planting seed (375 million pounds from 100,000 acres), the greatest quantity of aspirated grain dust in the U.S. sorghum seed industry would be 14 tons per year.
- The least amount would be 2.0 tons (based on the lowest seed estimate) and the most realistic quantity would be 8.25 tons per year.
- Hybrid sorghum seed is produced by planting a predominance (80% or more) of female lines (male sterile) with inter-dispersed rows of male pollinator lines.
- Over 96% of the U. S. sorghum planting seed is produced in Texas, primarily in the High Plains region by less than ten firms.
Global Sorghum Seed Production Statistics
- Over 95% of the U.S.-certified sorghum seed is produced in Texas (AOSCA), averaging 18,100 acres, and represents about 20% of the total seed production.
- The firms that participated in this survey handle over 87% of the U.S. sorghum seed (based on records from AOSCA and the TDA Seed Testing Laboratory).
- In Bangladesh, 3200 metric tons of sorghum grains are produced annually from about 4000 ha of land, and the average yield is 3.6 metric tons per hectare.
- Globally, sorghum is cultivated on 41 million hectares to produce 64.20 million tonnes, with productivity hovering around 1.60 tonnes per hectare.
- Sorghum as green foliage is very popular in most parts of north India and nearly 2.5 million hectare area is planted during Kharif.
Emerging Trends
- Forage Sorghum Innovation: A trend in forage sorghum includes the introduction of varieties like Double Team Forage Sorghum, which offers non-GMO, grassy weed management options. This advancement is particularly significant in North America, which is a major market for sorghum seeds.
- Hybrid and GM Varieties: There is a significant shift towards the development of hybrid sorghum varieties and genetically modified (GM) traits to enhance yield and resistance to environmental stresses. These innovations cater to the growing demands of the agricultural sector for more robust crop solutions.
- Biofuel Production: Sweet sorghum is gaining traction for its potential in biofuel production due to its high sugar content, which is suitable for ethanol production. The global push for renewable energy sources is driving interest in sorghum varieties that can be used to produce biofuels.
- Gluten-Free Applications: As consumer preferences shift towards healthier and gluten-free diets, sorghum is becoming more popular in food products. This trend is supported by sorghum’s nutritional profile, making it an appealing option for health-conscious consumers.
- Climate Resilience: Sorghum’s natural drought tolerance makes it an excellent crop for areas with challenging climates, particularly in regions experiencing water scarcity. This trait is increasingly important as global weather patterns become more erratic and water becomes a more precious resource.
Use Cases
- Livestock Feed: Sorghum is widely used as feed for livestock due to its nutritional value. It serves as a critical component in the diets of poultry, beef, and pork industries. The stems and foliage of sorghum are utilized for green chop, hay, silage, and pasture.
- Ethanol Production: Due to its high carbohydrate content, sorghum is increasingly used in ethanol production. It provides the same ethanol yield per bushel as other comparable feedstocks while consuming one-third less water, making it a more sustainable option for biofuel production.
- Gluten-Free Food Products: Sorghum’s gluten-free properties make it a valuable grain for people with gluten intolerance or celiac disease. It is used in various food products and can be found in over 1,400 products in the U.S. alone, ranging from breads and cereals to snacks.
- Biomass and Biofuel: Biomass sorghum is specifically cultivated for use in bioenergy production. Its quick growth and high biomass yield make it suitable for renewable energy sources like biofuels.
- Sweet Sorghum for Syrup: Sweet sorghum is grown for its stalks, which are processed to produce sorghum syrup. This syrup is used as a natural sweetener in various culinary applications, providing a healthier alternative to high-fructose corn syrup.
Major Challenges
- Water Scarcity and Drought: Sorghum is primarily grown in semi-arid regions where water availability is a significant challenge. Although sorghum is relatively drought-tolerant, prolonged dry spells can still affect its productivity and reduce the acreage farmers are willing to dedicate to this crop.
- Shift to Higher-Yielding Crops: In regions where water and land are limited, farmers often prefer to cultivate crops that offer a higher return on investment, such as rice, wheat, or corn. This trend has led to a decline in sorghum cultivation, as these crops generally provide better profitability.
- Pest and Disease Pressure: Sorghum crops face threats from various pests and diseases, which can significantly impact yield. For example, sorghum can be affected by diseases such as downy mildew or pests like stem borers and midge flies. Managing these challenges requires continual investment in research for resistant strains and effective treatment options.
- Market Volatility: The global trade dynamics for sorghum are influenced by fluctuating demand in key markets, such as China for animal feed or the U.S. for biofuel production. Changes in trade policies or shifts in demand can lead to market volatility, affecting farmers’ decisions on whether to plant sorghum.
- Adaptation to Climate Change: As weather patterns become more erratic, sorghum must adapt to a wider range of climatic conditions. While sorghum is known for its resilience, varying environmental stresses such as extreme temperatures or unseasonal rainfall pose ongoing adaptation challenges.
Market Growth Opportunities
- Increased Demand in Animal Feed: Sorghum’s high nutritional value makes it an excellent choice for animal feed. As global meat and dairy consumption rises, so does the demand for sorghum as a feed ingredient, which is expected to propel market growth.
- Expansion in Biofuel Production: Sorghum’s potential in biofuel production, especially ethanol, is increasingly recognized due to its high sugar content and efficiency as a bioenergy crop. With the global shift towards renewable energy, the demand for sorghum-based biofuels is likely to surge.
- Gluten-Free Market Penetration: Sorghum is naturally gluten-free, making it appealing in food markets, particularly for gluten-sensitive and health-conscious consumers. This trend presents significant opportunities for the introduction of sorghum-based products in the health and specialty food sectors.
- Climate Resilient Crop: Sorghum’s adaptability to harsh growing conditions such as drought makes it a critical crop in the face of climate change. This resilience allows it to be an ideal choice in arid and semi-arid regions, potentially increasing its cultivation and usage globally.
- Technological Advances in Agriculture: Continued advancements in agricultural technologies and hybrid seed development enhance sorghum yields and stress resistance. These innovations are crucial for meeting the growing global demand for food and sustainable agriculture practices.
Key Players Analysis
- Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM) is deeply committed to sustainable agricultural practices and has made significant strides in reducing its environmental impact. ADM has achieved net carbon-neutral status for its U.S. milling operations, emphasizing its commitment to sustainability.
- Advanta Seeds specializes in developing enhanced agricultural products including sorghum. They focus on creating varieties that are resilient and yield-rich, suitable for diverse global agricultural needs. Their innovations often target improved drought resistance and higher nutritional profiles, catering to the needs of both farmers and markets in challenging environments.
- Allied Seed LLC offers a variety of forage products, including sorghum, which are designed to provide high yields and superior performance. The company emphasizes traits like drought tolerance and nutritional value, making its products ideal for both livestock feed and biofuel production.
- American Seed Co. focuses on providing high-quality seeds, including sorghum, which are adapted to local conditions. Their sorghum seeds are selected for their yield potential and adaptability, ensuring effectiveness in diverse farming environments.
- Ardent Mills operates in the grain milling sector, producing a variety of flours and grains including sorghum. The company is focused on sustainability and health, offering products that meet the growing demand for wholesome, sustainably sourced food ingredients.
- Bayer CropScience LLC engages in the development of crops including sorghum through biotechnological and breeding innovations. They focus on creating crops that are more resilient to climatic stresses, pests, and diseases, thereby enhancing productivity and sustainability.
- Cargill, Incorporated is a major player in the global food industry, providing food, agriculture, financial, and industrial products and services. They deal in sorghum for a variety of uses including animal feed and food products, focusing on sustainable supply chains.
- Corteva Agriscience offers a range of agricultural products including sorghum seeds. They focus on technology-driven solutions for agriculture, developing seeds that provide farmers with high yields and resistance to environmental stresses.
- Ernst Conservation Seeds specializes in the production of native and naturalized seeds, including sorghum, aimed at ecological conservation projects. Their products are used in a variety of land restoration and conservation efforts, highlighting their commitment to environmental sustainability.
- Groupe Limagrain, through its subsidiary HM.CLAUSE focuses on the production of seeds for agriculture, including sorghum. They emphasize innovation and sustainability in their seed development processes to enhance global food security.
- KWS SAAT SE is known for its extensive research and development in plant breeding, producing high-quality sorghum seeds among other crops. Their focus is on innovation in genetic and biotechnological research to improve crop efficiency and adaptability.
- Mabele Fuels Pty Ltd is involved in the biofuel industry, utilizing sorghum as a key raw material for bioethanol production. Their work highlights the potential of sorghum in sustainable energy solutions.
- National Sorghum Producers is an organization that advocates for sorghum farmers, focusing on promoting the crop and enhancing its market presence. They provide resources and support to improve the competitiveness of sorghum in agricultural sectors.
- Nu Life Market is dedicated to producing gluten-free sorghum-based products, addressing the needs of consumers with dietary restrictions. Their focus on health and nutrition is evident in their range of sorghum flours and related products.
- Nufarm, under its brand Nuseed, offers a variety of agricultural products including sorghum. They focus on innovative agricultural solutions that provide added value to farmers and industries.
- Pannar Pty Ltd, a part of Corteva Agriscience, is known for its robust seed genetics. They offer a range of agricultural seeds including sorghum, tailored to enhance productivity and sustainability in diverse farming environments.
- Richardson Seeds, Ltd. specializes in sorghum seed production, focusing on high-performance seeds for both grain and forage uses. Their products are recognized for their quality and yield potential.
Conclusion
The Sorghum Seed market is uniquely positioned to capitalize on a range of growth opportunities, driven by its adaptability to harsh climates and its utility across various industries. With increasing emphasis on sustainable agriculture and the crop’s inherent drought resistance, sorghum seed is becoming an increasingly popular choice for farmers worldwide. Additionally, as global dietary trends shift towards gluten-free and health-conscious choices, sorghum’s versatility in food products presents further market potential.
Technological advancements in seed genetics and sustainable farming practices are likely to enhance yield and environmental resilience, making sorghum a key crop in the global pursuit of food security and sustainable agricultural practices. As the market continues to evolve, the strategic cultivation and utilization of sorghum seeds are expected to play a crucial role in meeting the nutritional needs of a growing global population while addressing the challenges of climate change.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





