Table of Contents
Overview
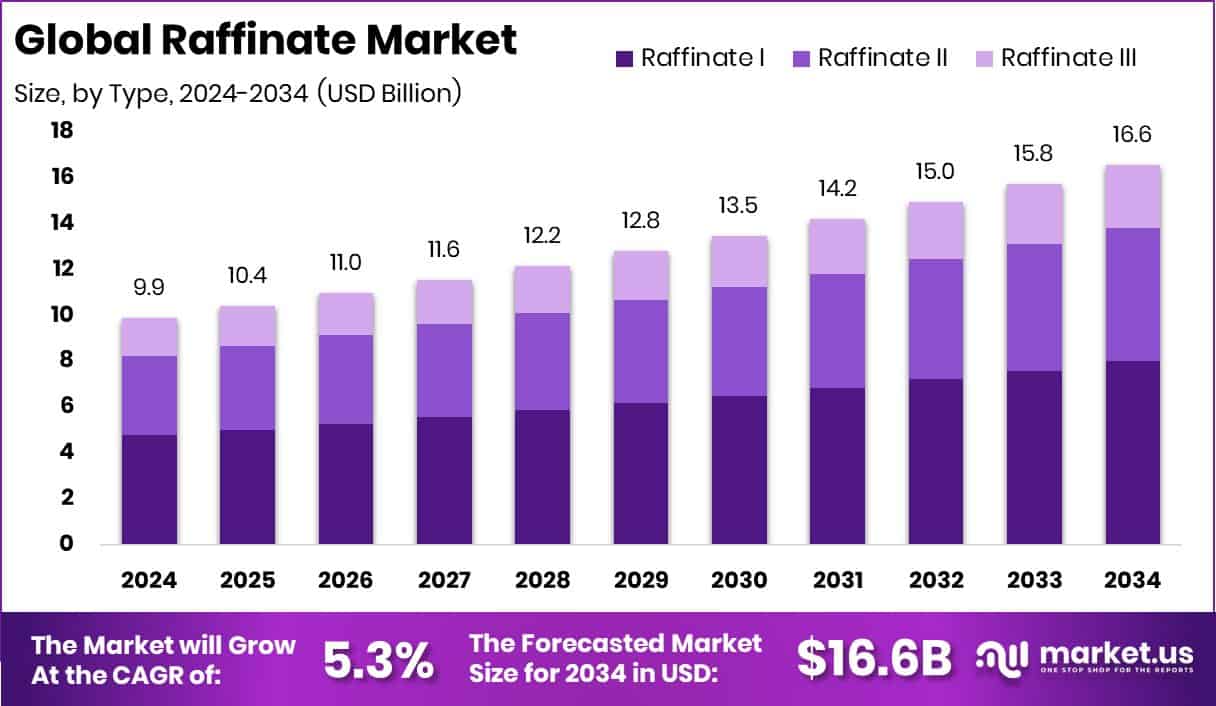
New York, NY – December 02, 2025 – The global raffinate market is on a steady growth path, projected to reach about USD 16.6 billion by 2034, rising from USD 9.9 billion in 2024, at a CAGR of 5.3% between 2025 and 2034. Asia Pacific continues to lead demand, supported by industrial expansion and holding a 46.20% market share.
Raffinate is the hydrocarbon stream remaining after extraction processes remove aromatics or specific compounds from feedstocks such as naphtha or kerosene. Due to its high paraffinic and olefinic content, it plays an essential role in lubricant blending, fuel formulations, and petrochemical intermediates. The raffinate market represents global demand for these cleaner, stable streams used across automotive, industrial, and energy-related applications.
Market growth is largely driven by increasing consumption of high-performance lubricants and the need for cleaner petrochemical inputs. Investment activity within the lubricant sector reinforces this trend. For example, Klüber Lubrication’s Rs 142 crore capacity expansion in India supports higher usage of refined raffinate to improve lubricant efficiency and stability.
Ongoing restructuring within the global lubricants industry is also shaping demand. BP’s plan to divest its Castrol business as part of its USD 20 billion asset-sale target, with interest from players such as Reliance and Aramco in a potential USD 10 billion transaction, highlights strategic shifts toward cleaner base materials.
Additionally, financial activity across the lubricant value chain supports raffinate demand. Gulf Oil Lubricants India’s promoter sold a 4% stake worth Rs 263 crore, while Golden Gate Capital completed a USD 479 million exit from PetroChoice, reflecting stronger capital flows that indirectly favor high-purity raffinate usage.
➤ Click the sample report link for complete industry insights: https://market.us/report/global-raffinate-market/request-sample/
Key Takeaways
- The Global Raffinate Market is expected to be worth around USD 16.6 billion by 2034, up from USD 9.9 billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.3% from 2025 to 2034.
- Raffinate I held a 48.2% share and dominated the Raffinate Market due to wide industrial usage.
- Solvent Extraction dominated the raffinate market with a 34.1% share, driven by cleaner processing demand.
- Automotive applications dominated the raffinate market with a 44.9% share, supported by rising lubricant needs.
- The Asia Pacific recorded a strong market valuation of USD 4.5 billion overall.
➤ Directly purchase a copy of the report – https://market.us/purchase-report/?report_id=166807
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2024) | USD 9.9 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 16.6 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 5.3% |
| Segments Covered | By Type (Raffinate I, Raffinate II, Raffinate III), By Application (Solvent Extraction, Lubricant Production, Fuel Additives, Chemical Intermediates, Others), By End-Use Industry (Automotive, Chemical, Oil and Gas, Others) |
| Competitive Landscape | ExxonMobil, Shell Plc, Chevron Corporation, TotalEnergies SE, Sinopec Limited, BASF SE, LyondellBasell Industries, INEOS Group, SABIC, Reliance Industries Limited |
Key Market Segments
By Type Analysis
In 2024, Raffinate secured a dominant position in the By Type segment of the Raffinate Market, accounting for a 48.2% share. This strong standing highlights its growing preference in applications that demand cleaner and more stable hydrocarbon streams with minimal aromatic content.
Raffinate is largely composed of paraffinic and olefinic structures, which makes it well suited for lubricant blending, fuel enhancement, and downstream petrochemical uses. These properties support improved oxidation resistance and thermal stability, helping manufacturers comply with stricter efficiency and emission requirements without significantly increasing processing steps.
The 48.2% share also reflects a broader industry shift toward refined feedstocks that enhance end-product quality while simplifying operational complexity. As producers aim to achieve higher performance standards with lower reformulation costs, Raffinate continues to stand out within the type-based classification, reinforcing its leadership and sustained demand across multiple industrial sectors.
By Application Analysis
In 2024, solvent extraction led the By Application segment of the Raffinate Market, securing a 34.1% share. This dominance is closely tied to its critical role in separating aromatics and other impurities from feedstocks, enabling refiners to produce clean paraffinic streams for fuels, lubricants, and petrochemical intermediates.
The process is widely favored for its high selectivity and ability to deliver reliable yields with consistent quality. These advantages help refiners meet rising performance expectations while supporting lower emission outcomes. Solvent extraction also offers operational stability across varied feedstock types, making it a dependable choice for large-scale refining operations.
The 34.1% share highlights continued industry reliance on this method to manufacture raffinate grades aligned with modern efficiency goals. Its flexibility and proven effectiveness position solvent extraction as a long-term leading application process within the raffinate market landscape.
By End-Use Industry Analysis
In 2024, the automotive sector dominated the By End-Use Industry segment of the Raffinate Market, accounting for a 44.9% share. This leadership is driven by the sector’s strong demand for clean paraffinic streams used in advanced lubricants, fuel additives, and performance-enhancing chemicals.
Raffinate plays a key role in improving engine efficiency by supporting better thermal stability, minimizing deposits, and enabling smoother engine performance in both passenger and commercial vehicles. Automakers increasingly depend on such refined inputs to align with stricter emission standards and higher durability expectations.
The 44.9% market share reflects a clear shift toward higher-purity base materials that enhance fuel and lubricant quality without compromising system efficiency. As vehicle technologies continue to evolve and regulatory pressure increases, the automotive segment remains the largest end-use contributor, reinforcing its long-term influence within the overall raffinate market.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific led the Raffinate Market in 2024 with a 46.20% share, valued at USD 4.5 billion. This dominance is driven by strong petrochemical operations, rising lubricant demand, and ongoing refinery modernization across key processing centers. Rapid growth in manufacturing and the automotive sector continues to generate steady demand for high-purity paraffinic streams used in fuels and performance lubricants.
North America records stable market expansion, supported by advanced refining technologies and a mature industrial base that consistently requires clean feedstocks for lubricant blending and chemical manufacturing. Europe maintains steady demand as strict environmental regulations encourage the use of low-aromatic materials and higher-quality extraction outputs.
The Middle East & Africa benefit from expanding refining capacity and increasing downstream diversification, which gradually increases raffinate usage. Latin America shows moderate growth, supported by evolving fuel standards and rising focus on improved lubrication performance in transportation and industrial activities.
Top Use Cases
- Base Oil for Lubricants: After removal of undesirable aromatic compounds via solvent extraction (or similar refining), the resulting raffinate is often used as a base oil feedstock for lubricants. Such base oils benefit from good thermal stability, lower volatility, and better oxidation resistance — essential traits for engine oils, industrial lubricants, and greases.
- Fuel Blending for Cleaner Fuels: Raffinate streams (especially low-octane, low-aromatic raffinates) can be blended into fuel pools to yield cleaner-burning or more stable fuels. Because raffinate tends to have lower reactivity compared to aromatic-rich fractions, it helps produce more stable fuel blends with favorable combustion and emissions characteristics.
- Petrochemical Feedstock (Olefins / Chemical Intermediates): Raffinate — rich in paraffins and olefins — serves as a feedstock for downstream petrochemical processes. These streams can be cracked or further processed to yield olefins (e.g. butenes, etc.) which are the building blocks for many chemicals, plastics, or synthetic materials.
- Production of High-Octane Additives (e.g. via Alkylation / MTBE): In certain configurations (especially with C4-type raffinate after removal of butadiene or butenes), raffinate can be directed into units that produce high-octane gasoline blending components. For instance, C4 raffinate is used in production of alkylates or additives like MTBE (where permitted), which help boost octane in gasoline blends.
- Feedstock for Specialty Chemicals, Solvents, Waxes, and Additives: Beyond fuel and lubricant base-stocks, raffinate-derived streams are used as raw material for various specialty chemicals: solvents, industrial oils, waxes, chemical intermediates, and additives for adhesives, coatings, or other industrial chemicals. This versatility stems from the relatively “clean” and stable hydrocarbon backbone in raffinate.
- Resource Efficiency and Waste Minimization in Refining / Petrochemical Integration: Using raffinate for these downstream applications helps maximize conversion efficiency from crude oil — what might otherwise be a lower-value byproduct or waste becomes a valuable feedstock. This contributes to overall resource efficiency in integrated refining-petrochemical operations.
Recent Developments
- In May 2024, ExxonMobil completed its acquisition of Pioneer. This move significantly expanded ExxonMobil’s upstream footprint, especially in the Permian Basin.
- In January 2024, Shell announced that its refinery at Wesseling (Germany) will stop crude oil distillation by 2025, and instead be converted into a facility focused on producing lubricant feedstock / base oils.
Conclusion
The raffinate market continues to play a vital role across the refining, lubricant, fuel, and petrochemical value chains due to its cleaner composition and stable performance characteristics. Industries increasingly prefer raffinate as it supports improved product quality, operational efficiency, and compliance with environmental norms.
Ongoing refinery upgrades and downstream integration are strengthening its adoption across both mature and emerging regions. Demand is further supported by growth in automotive, industrial manufacturing, and energy applications that require reliable paraffinic feedstocks.
As refiners and chemical producers focus on efficiency, sustainability, and higher-value outputs, raffinate remains a strategically important material that supports diversified end uses and long-term industry resilience.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





