Table of Contents
Overview
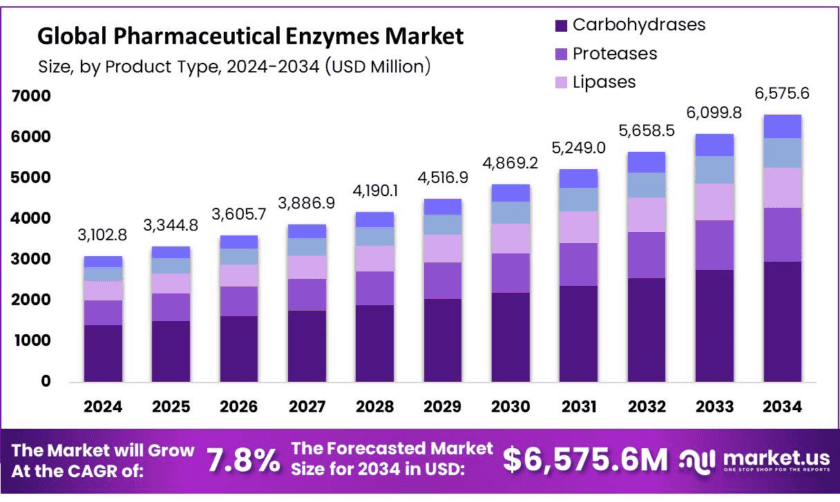
New York, NY – Dec 10, 2025 – The global pharmaceutical enzymes market is set for steady expansion, with its value projected to reach approximately USD 6,575.6 million by 2034, up from USD 3,102.8 million in 2024. This growth reflects a solid CAGR of 7.8% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, Europe emerged as the leading regional market, accounting for more than 39.6% of global revenue and generating around USD 1.4 billion, supported by strong biopharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities and regulatory support for bio-based drug development.
Enzymes have become essential to the pharmaceutical industry, playing a vital role in drug synthesis, formulation, and quality control. As biological catalysts, they offer high specificity and efficiency while supporting environmentally sustainable production processes. The growing focus on green chemistry, cost reduction, and precision-driven drug manufacturing has significantly boosted enzyme adoption across traditional pharmaceutical production as well as advanced biotechnology-based applications.
As active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), enzymes are reshaping modern drug development by enabling more targeted and efficient therapies. Their use supports personalized medicine approaches, reduces unwanted side effects, and contributes to cleaner manufacturing methods. Although challenges such as enzyme stability and complex regulatory requirements persist, ongoing innovation in enzyme engineering continues to unlock new therapeutic possibilities for treating complex and chronic diseases, strengthening their role in healthcare advancement.
Innovation in enzyme technology is further accelerating market growth. For example, in April 2025, eXoZymes Inc. introduced BioClick, a program focused on advancing enzyme engineering for complex chemical reactions. Backed by a USD 300,000 grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the initiative aims to improve pharmaceutical and bio-based chemical production efficiency.
Among the most commonly used enzymes in pharmaceuticals are proteases, lipases, and amylases. Proteases support treatments for clotting disorders and digestive conditions by breaking proteins into amino acids. Lipases help manage fat metabolism and lipid-related diseases, while amylases aid in starch digestion for digestive therapies. Together, these enzymes highlight the broad functionality and therapeutic value of enzyme-based pharmaceutical solutions.
Key Takeaways
- The global pharmaceutical enzymes market was valued at USD 3,102.8 million in 2024
- In 2024, among product type, carbohydrases accounted for the largest market share of 45.2%
- Among source, microorganisms held major market share of 70.2% in 2024
- By formulation, in 2024 powder pharmaceutical enzymes accounted for the largest market share of 61.8%
- By production method, submerged fermentation has dominated the market in 2024 with 71.2% market share
- In 2024, North America led the global pharmaceutical enzymes market with substaintial market share of 36.8%. Furthermore, in the region US was the major contributor with market value of USD 1,024.2 million in the 2024.
➤ For a deeper understanding, click on the sample report link: https://market.us/report/pharmaceutical-enzymes-market/free-sample/
Report Scope
| Market Value (2024) | USD 3,102.8 Mn |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 6,575.6 Mn |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 7.8% |
| Segments Covered | By Product Type (Carbohydrases, Proteases, Lipases, Polymerases & Nucleases, Others), By Source (Plants, Animals, Microorganisms), By Formulation (Powder, Liquid), By Production Method (Submerged Fermentation, Solid-state Fermentation) |
| Competitive Landscape | Novozymes / Novonesis, Codexis, Inc., BASF SE, DSM (DSM-Firmenich), Amano Enzyme Inc., Biocatalysts Ltd., BRAIN Biotech AG, Sanofi, Merck KGaA, Asymchem Inc., Halozyme Therapeutics, Kerry Group plc, Aumgene Biosciences, Bioseutica BV, Infinita Biotech Private Limited, Other Key Players |
➤ Directly purchase a copy of the report – https://market.us/purchase-report/?report_id=161488
Key Market Segments
Product Type Analysis
In 2024, carbohydrases represented the largest product category in the global pharmaceutical enzymes market, accounting for about 45.2% of overall demand. This leadership is mainly attributed to their extensive use in drug formulation, excipient modification, and active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) production. Enzymes such as amylases and cellulases are particularly important due to their ability to efficiently convert complex carbohydrates into simpler and bioactive compounds required in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Amylases are widely applied in developing starch-based excipients that improve solubility, stability, and controlled drug release, supporting advanced dosage forms. At the same time, cellulases are increasingly used to modify cellulose-based excipients, improving tablet binding strength and drug bioavailability, while also supporting biotransformation processes for high-value pharmaceutical intermediates.
Source Analysis
In 2024, microorganisms dominated the pharmaceutical enzymes market, contributing approximately 70.2% of total share. Bacteria and fungi remain the most preferred enzyme sources due to their ability to deliver high enzyme yields through cost-efficient, large-scale fermentation. Their genetic flexibility allows manufacturers to enhance enzyme stability, catalytic efficiency, and therapeutic precision through strain optimization. Microbial enzymes play a crucial role across multiple therapeutic areas, including oncology, cardiovascular diseases, inflammatory disorders, and metabolic conditions. Well-known examples include L-asparaginase for leukemia treatment, streptokinase and nattokinase for clot dissolution, and collagenase for wound healing. Emerging microbial enzymes, such as EndoS, continue to expand the clinical potential and innovation scope within enzyme-based therapies.
Formulation Analysis
The powder formulation segment led the global pharmaceutical enzymes market in 2024, holding a dominant 61.8% market share. This dominance is driven by the superior stability and longer shelf life of powdered enzymes compared to liquid alternatives. Powder formulations maintain enzymatic activity under varying storage and transportation conditions, making them suitable for global supply chains. Additionally, powdered enzymes offer greater flexibility in drug formulation, allowing accurate dosing and controlled integration into tablets, capsules, and dry powder inhalers. Their ease of storage, transportation, and reconstitution further contributes to reduced logistics costs and enhanced manufacturing efficiency, supporting their widespread adoption across the pharmaceutical sector.
Production Method Analysis
In 2024, submerged fermentation (SmF) emerged as the leading production method in the pharmaceutical enzymes market, accounting for approximately 71.2% of total enzyme output. This method is favored due to its scalability, tight process control, and consistent enzyme quality. SmF involves cultivating microorganisms in liquid media under controlled pH, temperature, and oxygen levels, enabling high yields and uniform production. It supports the manufacturing of key enzymes such as proteases, lipases, amylases, and cellulases, which are essential in treating cancer, cardiovascular, and digestive disorders. The method also allows genetic optimization of microbial strains, ensuring high reproducibility and compliance with strict pharmaceutical quality standards.
List of Segments
By Product Type
- Carbohydrases
- Amylases
- Cellulases
- Others
- Proteases
- Lipases
- Polymerases & Nucleases
- Others
By Source
- Plants
- Animals
- Microorganisms
By Formulation
- Powder
- Liquid
By Production Method
- Submerged Fermentation
- Solid-state Fermentation
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America held the leading position in the global pharmaceutical enzymes market, accounting for approximately 36.8% of total market share. The United States dominated regional demand, contributing around 89.7% of pharmaceutical enzyme consumption, reflecting its strong position as a global center for biopharmaceutical research, development, and manufacturing. The U.S. continues to lead worldwide biopharmaceutical innovation, with companies investing close to USD 96 billion in research and development in 2023, according to the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA). Notably, R&D spending represented over 20% of total biopharmaceutical sales during the same year, highlighting the industry’s strong focus on scientific progress and advanced drug development.
The overall economic contribution of the U.S. biopharmaceutical sector remains significant. In 2022, exports from majority foreign-owned biopharmaceutical companies based in the U.S. exceeded USD 25 billion, while these firms invested nearly USD 26 billion in domestic R&D activities. Additionally, foreign direct investment in pharmaceuticals and medicines reached approximately USD 503.4 billion in 2023, reinforcing the United States’ attractiveness as a leading destination for global pharmaceutical investment and a key driver of enzyme innovation and commercialization.
Top Use Cases
Digestive & Metabolic Disorder Treatments: Enzymes such as proteases, lipases, and amylases are widely used in medicine to support digestion and treat metabolic deficiencies. For example, mixtures of proteases, lipases and amylases help people with pancreatic insufficiency to digest proteins, fats, and starches properly. These therapeutic enzymes mimic natural digestive processes — improving nutrient absorption and reducing gastrointestinal disorders.
Cancer Therapy (Enzyme-Based Oncology Drugs): Some enzymes serve directly as therapeutic agents in cancer treatment. For instance, L‑asparaginase is used to treat certain types of leukaemia by depriving cancer cells of asparagine, an amino acid vital for their growth. This enzyme-based therapy exemplifies how enzymes function as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), offering targeted, efficient treatment with high biochemical specificity.
Fibrinolysis and Cardiovascular Therapy: Enzymes like Streptokinase, and other fibrinolytic enzymes, are used to break down blood clots — a critical function in treating heart attacks, strokes, and other thrombotic disorders. By converting inactive precursors into active clot-dissolving molecules, these enzymes restore normal blood flow and prevent life-threatening complications. Their high specificity and catalytic speed make them powerful tools for emergency cardiovascular care.
Anti-Inflammatory and Tissue Repair Applications: Therapeutic enzymes — including proteases, collagenases, and other hydrolases — are increasingly applied as anti-inflammatory agents and for wound healing or tissue remodeling. For example, certain enzymes degrade inflammatory mediators, reduce oxidative stress, or help clear damaged proteins, offering an alternative to conventional anti-inflammatory drugs with potentially fewer side effects.
Biocatalysis in Drug Synthesis & Manufacturing: Beyond direct therapeutic use, enzymes play a vital role in drug development and synthesis. Their high specificity allows complex chemical transformations under mild conditions — often more efficient, cleaner, and environmentally friendly than traditional chemical synthesis. This makes them essential not only as APIs but also as enabling tools in the production of modern pharmaceuticals, especially for chiral drugs and advanced biopharmaceutical compounds.
Recent Developments
Novonesis (formerly Novozymes) — In January 2024, Novozymes merged with Chr. Hansen to form Novonesis, creating a global biosolutions leader with an estimated annual revenue of about €3.7 billion. While Novonesis is best known for agricultural and industrial biosolutions, its enzyme-production heritage positions it to supply enzymes potentially usable in pharmaceutical and biotechnological applications.
Codexis, Inc. — In 2025, Codexis reported US$15.3 million revenue in Q2, driven primarily by growing demand for enzymes in its Pharma Biocatalysis business and adoption of its proprietary ECO Synthesis platform for siRNA manufacturing. Using its proprietary enzyme engineering platform, Codexis delivers custom-designed, high-performance enzymes that enable greener and more efficient manufacturing of APIs, RNA therapeutics, and diagnostics — offering improved yields and reduced waste compared with traditional chemical processes.
BASF SE — As of 2025, BASF continues to be a major player in the global enzyme landscape, though recent strategic moves have shifted its focus. In mid-2025, BASF announced it is evaluating strategic options for its feed enzymes business — a division that historically included phytase, xylanase, glucanase and mannanase — which reportedly generates around USD 150–200 million in annual sales. While BASF has recently divested its bioenergy-enzyme operations and sold its food & health performance ingredients business, the shift suggests a re-alignment of its enzyme portfolio rather than a complete exit, indicating ongoing re-evaluation of its role in enzyme supply.
DSM‑Firmenich — In 2024–2025, DSM-Firmenich remained active in enzyme-based solutions, especially targeting health and nutrition. Their enzyme products include digestive aids such as lactase and proline-specific endopeptidase for lactose and gluten intolerance, under brands like Tolerase® L and Tolerase® G. However, in February 2025 the company sold its stake in the long-standing Feed Enzymes Alliance to Novonesis for €1.5 billion, concluding a 25-year collaboration and repositioning its business away from feed-enzyme production.
Amano Enzyme Inc. — As of 2025, Amano Enzyme continues to strengthen its position in the pharmaceutical and biotech enzyme space, offering “medical-grade” and “green-chemistry” enzymes for API synthesis and healthcare applications. Their enzyme catalogue supports tailored synthesis and biocatalysis under mild, sustainable conditions — helping drug makers reduce waste and improve reaction specificity.
Biocatalysts Ltd. — In 2025, Biocatalysts Ltd. showcased its commitment to pharma-grade biocatalysis at major industry events, highlighting innovations in enzyme discovery, strain development, and large-scale enzyme production for pharmaceutical and biotech clients. Their global operational reach and expertise in enzyme scaling help support drug development, sustainable manufacturing, and enzymatic biotransformations in active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) synthesis.
BRAIN Biotech AG — In 2025, BRAIN Biotech strengthened its role in the pharmaceutical-enzyme sector by offering end-to-end enzyme solutions — from discovery and microbial strain engineering to full-scale bioprocess production — under its “BRAINBiocatalysts Life Science Solutions” platform. Its expanded yeast-based production platform (using Komagataella phaffii) enables high-yield enzyme and protein output (in the double-digit g/L range) for industrial and pharma clients, helping accelerate drug manufacturing and biocatalysis efficiency.
Sanofi — In 2024, Sanofi’s pharma-division continued to drive the enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) field with therapies like avalglucosidase alfa (for Pompe disease) and imiglucerase (for Gaucher disease). The company’s strong 2025 performance — with Q1 sales growth of 9.7% and increased R&D investment — underpins its commitment to rare-disease enzyme therapies and supports continued innovation in enzyme-based treatments.
Merck KGaA — In 2025, Merck KGaA’s life-sciences arm (branded as MilliporeSigma in the U.S. and Canada) further expanded its enzyme and bioprocessing capabilities by acquiring Mirus Bio for about US$ 600 million, enhancing its viral-vector manufacturing and enzyme-based processing portfolio. This strategic move reinforces Merck’s push into advanced biologics and gene therapy production, underlining its commitment to providing enzyme-driven solutions and scalable bioprocessing services globally.
Asymchem Inc. — In 2025, Asymchem continued to grow as a leading global CDMO (contract development and manufacturing organization), offering therapeutic enzyme development and biocatalysis services through its API and therapeutic-enzyme platforms. The company supports both small molecules and biologics, delivering enzyme-enabled drug synthesis and biotransformation services, which help pharmaceutical clients achieve efficient, scalable, and quality-controlled production of APIs and enzyme-based therapies.
Halozyme Therapeutics — In 2025, Halozyme strengthened its position in the pharmaceutical enzyme world by advancing its proprietary enzyme-based drug-delivery technology, ENHANZE®. Using its recombinant human hyaluronidase (rHuPH20), Halozyme enables fast, high-volume subcutaneous injection of biologic drugs — improving patient convenience and reducing treatment burden. The company raised its 2025 revenue guidance to about USD 1.3 billion, with royalties expected between USD 825–860 million, underscoring growing adoption of enzyme-enabled delivery platforms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pharmaceutical enzymes have become a vital pillar of modern drug development and healthcare due to their high efficiency, selectivity, and eco-friendly nature. They are widely used as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and as biocatalysts in drug manufacturing, helping reduce production time, costs, and environmental impact.
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), enzyme-based therapies play an increasing role in treating cancer, cardiovascular disorders, metabolic diseases, and rare genetic conditions. Additionally, enzyme-driven biocatalysis supports greener pharmaceutical production, aligning with global sustainability goals. With rising investments in biotechnology, personalized medicine, and enzyme engineering, pharmaceutical enzymes are expected to remain critical to innovation, safer therapies, and sustainable pharmaceutical manufacturing worldwide.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





