Table of Contents
Overview
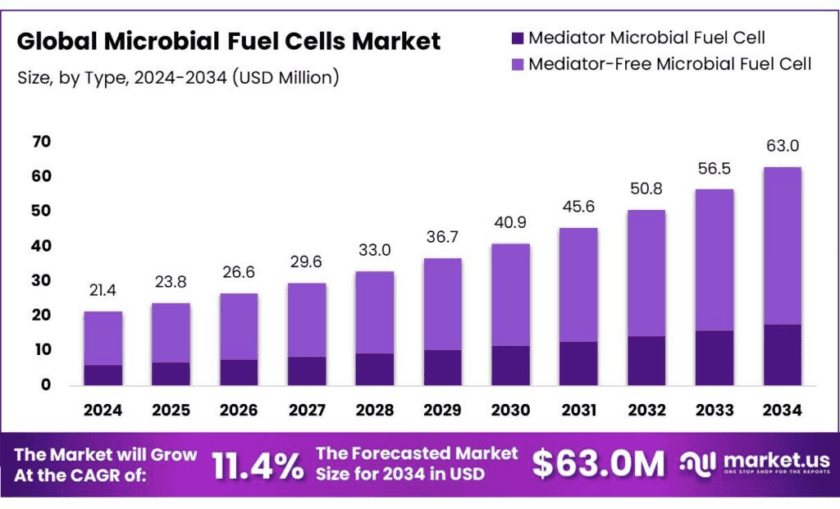
New York, NY – Oct 30, 2025 – The global microbial fuel cells (MFCs) market is projected to reach USD 63.0 million by 2034, increasing from USD 21.4 million in 2024, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.4% from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region held a dominant position, accounting for 47.3% of the total market share, with a revenue value of USD 10.1 million. The strong regional performance is supported by rapid technological advancements, government-led renewable energy programs, and growing wastewater treatment needs in countries such as China, Japan, and India.
Technological advancements have significantly improved MFC performance over the past decade. Early systems produced only tens to hundreds of milliwatts per square meter (mW/m²), whereas modern laboratory-scale systems have achieved power densities exceeding 1 watt per square meter (W/m²). Notably, graphite-sheet electrodes have demonstrated outputs of approximately 1,771 mW/m², while other engineered anode systems have reached around 750 mW/m². Although these figures remain below commercial-scale requirements, they indicate steady improvements in electrode efficiency and design architecture.
Industrial pilot projects, particularly in Europe, have demonstrated the use of MFCs for decentralized sanitation and remote wastewater treatment applications, achieving simultaneous chemical oxygen demand (COD) reduction and low-power electricity generation. Many of these initiatives are part of EU-funded programs aimed at cost-efficient off-grid decontamination and sustainable energy recovery. Policy support continues to strengthen the commercialization pathway for MFCs.
- In November 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy’s ARPA-E announced a USD 36 million funding program to recover valuable resources such as ammonia and metals from wastewater, a move that aligns closely with microbial electrochemical systems. Similarly, Europe’s Horizon initiatives have supported sludge-to-energy and waste-to-power projects, fostering a robust ecosystem of researchers, suppliers, and industrial partners contributing to the maturation of the microbial fuel cell industry.
Key Takeaways
- Microbial Fuel Cells Market Market size is expected to be worth around USD 63.0 Million by 2034, from USD 21.4 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 11.4%.
- Mediator-Free Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 72.4% share.
- Wastewater Treatment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 44.2% share.
- Government & Municipal sectors held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 31.3% share of the Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs) market.
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) region holds a dominant market position in the Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs) sector, capturing 47.3% of the market share, valued at USD 10.1 million.
➤ For a deeper understanding, click on the sample report link: https://market.us/report/microbial-fuel-cells-market/free-sample/
Report Scope
| Market Value (2024) | USD 21.4 Mn |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 63.0 Mn |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 11.4% |
| Segments Covered | By Type (Mediator Microbial Fuel Cell, Mediator-Free Microbial Fuel Cell), By Application (Wastewater Treatment, Power Generation, Biosensor, Others), By End User (Agriculture, Food and Beverage, Government and Municipal, Healthcare, Military, Others) |
| Competitive Landscape | MICRORGANIC TECHNOLOGIES, SAINERGY TECH INC, JSP ENVIRO, CASCADE Clean Energy, Inc., Frontis Energy, Kurita water industries ltd, AQUACYCL, Biologois |
➤ Directly purchase a copy of the report – https://market.us/purchase-report/?report_id=159715
Key Market Segments
1. By Type Analysis – Mediator-Free Microbial Fuel Cells Dominate with 72.4% Market Share in 2024
In 2024, Mediator-Free Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs) accounted for a dominant 72.4% market share, reflecting their increasing preference across industries. These systems have gained prominence due to their cost-effectiveness and eco-friendly design, as they eliminate the need for costly chemical mediators and rely entirely on microorganisms for electron transfer. This not only reduces operational expenses but also minimizes environmental impact. The efficiency of these systems has further improved through advancements in microbial strains and electrode materials, enhancing overall power generation capacity. Looking ahead to 2025, the segment is projected to expand further as technological innovations continue to optimize performance and reduce costs. With rising investments in renewable energy and wastewater treatment infrastructure, Mediator-Free MFCs are expected to play a critical role in decentralized and off-grid clean energy applications.
2. By Application Analysis – Wastewater Treatment Leads with 44.2% Market Share in 2024
In 2024, the wastewater treatment segment emerged as the leading application for Microbial Fuel Cells, holding more than a 44.2% share of the market. This dominance is driven by the increasing global focus on sustainable wastewater management and energy recovery solutions. MFCs provide a dual advantage in this sector—simultaneously treating wastewater by decomposing organic matter and generating electricity from the process. This makes them particularly valuable for industries and municipalities aiming to reduce operational costs while meeting environmental compliance standards. Rising concerns over water pollution, resource scarcity, and stringent environmental regulations are fueling adoption across developed and emerging economies. As technology matures, the wastewater treatment application is projected to expand further in 2025, supported by large-scale pilot projects and government-backed sustainability initiatives aimed at integrating MFCs into municipal wastewater infrastructure.
3. By End-User Analysis – Government & Municipal Sectors Dominate with 31.3% Market Share in 2024
The government and municipal sectors dominated the Microbial Fuel Cells market in 2024, capturing a 31.3% market share. This segment’s growth is primarily driven by the rising need for sustainable wastewater treatment and energy-efficient public infrastructure. MFC technology provides a strategic advantage for municipalities, enabling simultaneous wastewater purification and electricity generation, thereby reducing dependency on external energy sources. Governments across the globe are adopting MFC systems as part of broader sustainability and carbon reduction programs, supported by policy initiatives and financial incentives. In addition, increased public-sector funding and research collaborations are accelerating implementation within wastewater treatment plants and decentralized sanitation systems. By 2025, the share of government and municipal users is expected to rise further as MFCs prove their reliability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness in real-world environmental management applications.
List of Segments
By Type
- Mediator Microbial Fuel Cell
- Mediator-Free Microbial Fuel Cell
By Application
- Wastewater Treatment
- Power Generation
- Biosensor
- Others
By End User
- Agriculture
- Food and Beverage
- Government & Municipal
- Healthcare
- Military
- Others
Regional Analysis
Asia-Pacific (APAC) Dominates the Microbial Fuel Cells Market with 47.3% Share, Valued at USD 10.1 Million in 2024
In 2024, the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region emerged as the leading market for Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs), capturing a 47.3% share and generating a market value of approximately USD 10.1 million. This strong regional performance is driven by rapid industrialization, rising urban population, and an increasing commitment to sustainable technologies in key economies such as China, India, and Japan. These countries are at the forefront of MFC adoption due to large-scale industrial operations, significant wastewater generation, and proactive government initiatives promoting clean energy and wastewater recycling.
Across APAC, MFCs are being increasingly recognized as a viable solution to combat water scarcity, pollution, and energy inefficiency. Governments in the region have expanded investments in wastewater treatment infrastructure, viewing MFCs as a cost-efficient and eco-friendly alternative to energy-intensive traditional systems. Furthermore, the ability of MFCs to enable decentralized power generation makes them particularly beneficial for off-grid and rural communities, where reliable access to electricity remains limited. With continuous R&D investments and policy backing, the APAC market is expected to strengthen its leadership position by 2025, supported by growing applications in bioenergy and environmental remediation sectors.
Top Use Cases
Wastewater treatment + energy co-production: MFCs can treat organic wastewater while producing electricity, reducing the load on conventional treatment and offsetting plant energy use. Pilot and industrial demonstrations report COD removal comparable to conventional pretreatment and measurable power output; lab and pilot systems have shown areal power densities from tens of mW/m² up to >1 W/m².
Industrial process effluent management (food, brewery, sugar, animal farms): Food & beverage and agro-processing plants have deployed MFC-based units as pretreatment or polishing steps, reporting operational cost reductions (20–60% in Aquacycl case studies) and simultaneous reductions in GHGs and chemical inputs. Such installations are attractive where effluents are high-strength and onsite energy offsets are valuable.
Decentralised sanitation and off-grid electrification: MFC systems can be sited at remote or off-grid locations (small communities, farms) to provide low-power electricity for sensors, pumps or lighting while treating waste. Demonstrations and EU pilots target decentralized sanitation and remote wastewater polishing as practical near-term use cases.
Nutrient recovery and resource valorisation: Advanced MFC architectures can be coupled with recovery units (e.g., ammonia recovery) so that wastewater becomes a source of recovered chemicals and energy. Recent public funding (ARPA-E’s USD 36 million RECOVER program, Nov 2024) accelerates technologies that recover ammonia and critical materials from wastewater—an adjacent push that benefits MFC developers.
Industrial onsite power for auxiliaries and sensors: Field demonstrations (for example Kurita’s pilot) have shown MFC arrays powering instrumentation and small electrical devices continuously from real wastewater, with reported power generation metrics at pilot scale up to ~200 W/m³ reaction-volume in demonstration tests. This validates MFCs as a potential onsite power source for low-energy loads.
Process intensification: replace or reduce aeration energy: MFCs can reduce or replace energy-intensive aeration by using electroactive biofilms to degrade organics. Some vendors report reduced aeration energy by 80–90% in specific pilot configurations, improving overall plant energy balance when used as a pretreatment step.
Recent Developments
MICROrganic Technologies, based in Troy, New York, specializes in microbial fuel cell (MFC) systems for wastewater treatment and energy recovery. In 2024 the company highlighted its VIVA™ MFC technology, which claims to reduce aeration energy by 85-90%, cut nitrogen by 35-40%, and generate additional clean DC power equating to 15-20% of process energy. This puts MICROrganic at the forefront of the MFC sector, offering cost-effective, scalable treatment solutions aligned with both sustainability and operational-efficiency objectives.
Sainergy Tech, Inc., with operations in the US and India, develops fuel-cell and microbial-fuel-cell (MFC) components—including gas diffusion layers, catalyst-coated membranes and complete MFC units. While full commercial revenue figures for 2023/24 are not clearly disclosed, Sainergy markets “Microbial Fuel Cell – Single & Double Chamber MFCs” among its instrument offerings. As a market-research analyst would note, Sainergy’s component-level focus positions it well as a supplier to the broader MFC ecosystem, supporting the trend toward scalable and modular MFC deployments in industrial and infrastructure applications.
JSP Enviro, founded in 2016 and based in India, develops microbial fuel cell (MFC) systems that treat industrial wastewater while generating electricity. Their technology targets small-scale effluents like those from dyeing plants with loads as low as 100 kg BOD/day, and is designed to be energy-positive and carbon-neutral. While specific 2023-24 revenue data is not publicly detailed, JSP Enviro has been recognised as India’s first startup in this space to win EIT Climate-KIC funding, signalling strong market positioning and technological readiness.
Cascade Clean Energy, Inc., a U.S.-based clean-tech firm founded in 2008, develops bioelectrochemical systems including microbial fuel cells that convert organic-rich waste into electricity and clean water. According to public company profiles, the firm focuses on designing custom reactors that maximise energy recovery from wastewater—highlighting that 99% of wastewater treatment plants currently recover zero energy. Although detailed 2023 or 2024 revenue numbers for its MFC segment aren’t listed, Cascade’s focus on integrated waste-to-energy MFC solutions positions it as a key participant in the emerging commercialisation of the MFC market.
Frontis Energy, a German clean-tech startup founded in 2018, develops advanced microbial fuel cells (MFCs) tailored for wastewater treatment and energy recovery. The company reports achieving ammonium removal at rates up to 55 g/m²/day and near-complete (97 %) removal of a 0.3 % solution in pilot systems. While full-year revenue figures for 2023 or 2024 are not publicly detailed, Frontis’ scaling efforts and membership in the Solar Impulse Foundation underscore its growing role in the MFC value chain.
Kurita Water Industries Ltd. has made notable progress in the microbial fuel cell sector, conducting a demonstration in November 2024 where actual wastewater was used to generate electricity at cell volumes achieving up to 550 W/m³ and 0.6–0.8 Wh/g-CODCr from organic matter removal. This upsized system reflects Kurita’s ambition to integrate MFCs into industrial wastewater treatment and energy-harvesting applications, aligning with its medium-term goal of near-zero-CO₂ wastewater treatment systems.
Aquacycl, founded in 2016 and based in California, offers its patented BioElectrochemical Treatment Technology (BETT®) which uses microbial fuel cells (MFCs) to treat ultra-high-strength organic wastewater while generating direct electricity. The system claims to reduce wastewater management costs by 20-60% and is notably applied in food & beverage and confection industries. Though publicly disclosed exact revenue for 2023 or 2024 is not available, the company is recognised as a commercial-ready MFC provider addressing industrial wastewater challenges.
Conclusion
In conclusion, microbial fuel cells (MFCs) represent a promising technological bridge between wastewater treatment and renewable energy generation. Research examines power densities from range-varying studies—frequently between 0.2 to 200 W/m³ and areal power densities up to 2,000 mW/m² under ideal conditions. While still far from commercial scale in many cases, the dual benefits of organic removal and electricity recovery give MFCs strong potential as part of sustainable infrastructure. As water-energy-waste nexus pressures grow globally, MFCs stand as a credible innovation that deserves increased investment and deployment.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





