Table of Contents
Introduction
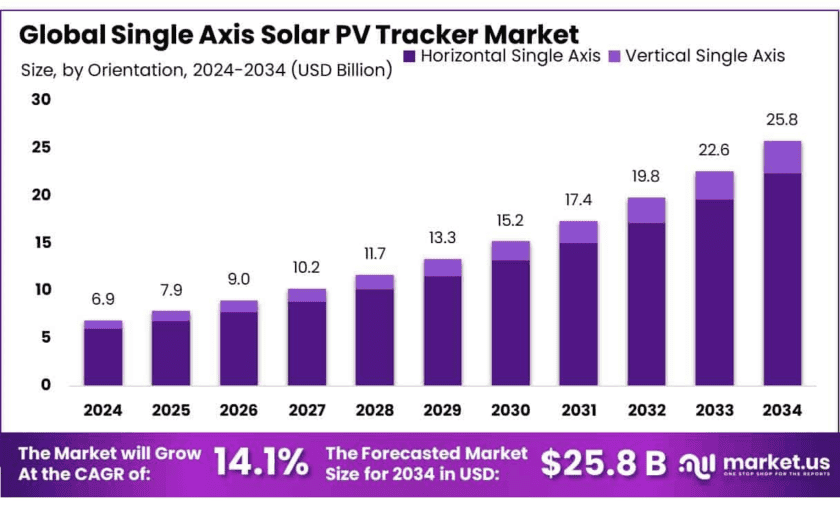
The global Single Axis Solar PV Tracker Market is experiencing significant growth, with an expected market value of USD 25.8 billion by 2034, up from USD 6.9 billion in 2024. This growth reflects a (CAGR) of 14.1% from 2025 to 2034. Single-axis solar trackers, which adjust the position of solar panels to follow the sun’s movement, are becoming increasingly popular due to their ability to enhance energy efficiency and reduce costs. Key drivers of growth include rising demand for renewable energy, technological advancements, and favorable government policies supporting sustainable energy solutions.
Arctech Solar has secured a significant 1.5 GW supply agreement for its SkyLine II single-axis tracker system with PowerChina for the Al Ajban project in the UAE. Array Technologies has initiated the construction of a new manufacturing facility in Albuquerque, New Mexico, aiming to produce 100% domestically sourced trackers by the first half of 2025.
Canadian Solar reported module shipments of 8.2 GW in Q4 2024, marking a 1% increase year-over-year. The company continues to integrate single-axis trackers into its large-scale projects, such as the 47.6 MW solar plant in North Carolina.
Key Takeaways
- Single Axis Solar PV Tracker Market size is expected to be worth around USD 25.8 Billion by 2034, from USD 6.9 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 14.1%.
- Horizontal Single Axis held a dominant market position, capturing more than an 86.7% share.
- Monocrystalline Panels held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 53.8% share.
- Hybrid Trackers held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 54.1% share.
- Electric Drive held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.3% share.
- Utility-Scale held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 72.6% share.
- Asia Pacific (APAC) region stands as the dominant player in the global single-axis solar photovoltaic (PV) tracker market, commanding a substantial share of approximately 46.1%, equating to an estimated market value of USD 3.1 billion in 2024.
➤ 𝐒𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐑𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐞𝐬𝐭: 𝐔𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐜𝐤 𝐕𝐚𝐥𝐮𝐚𝐛𝐥𝐞 𝐈𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐭𝐬 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐘𝐨𝐮𝐫 𝐁𝐮𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐞𝐬𝐬: https://market.us/report/single-axis-solar-pv-tracker-market/free-sample/
Report Scope
| Market Value (2024) | USD 6.9 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 25.8 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 14.1% |
| Segments Covered | By Orientation (Horizontal Single Axis, Vertical Single Axis), By Panel Type (Monocrystalline Panels, Polycrystalline Panels, Thin-Film Panels), By Tracker Type (Fixed-tilt Trackers, Tilt-only Trackers, Hybrid Trackers), By Mechanism (Mechanical Drive, Electric Drive, Hydraulic Drive), By Application (Utility-Scale, Commercial and Industrial, Residential) |
| Competitive Landscape | Arctech Solar, Array Technologies, Canadian Solar, Valmont Industries, Inc., DEGERenergie, First Solar, Fronius International, Hanwha Group, JA Solar, JinkoSolar, Kyocera Corporation, Nextracker, PV Hardware, Soltec Power Holdings, SunPower Corporation, Trina Solar |
Emerging Trends
- Integration of Bifacial Solar Modules: Combining bifacial solar modules with single-axis trackers has been shown to reduce the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) by approximately 16% compared to traditional monofacial systems. This integration enhances energy capture efficiency, leading to higher energy yields and improved economic viability of solar projects.
- Advancements in Tracker Technology: Innovations in tracker design are focusing on enhancing durability and performance. For instance, companies are developing trackers that can withstand extreme weather conditions, such as high winds and heavy snow, by incorporating features like high-tilt stow capabilities. These advancements aim to improve the reliability and lifespan of solar installations.
- Cost Reduction and Economies of Scale: The solar tracker industry is benefiting from economies of scale, leading to reduced costs. In the U.S., for example, 94% of new utility-scale PV capacity in 2022 utilized single-axis tracking systems, driven by cost-effective solutions and supportive policies.
- Focus on Sustainability: Companies are increasingly adopting sustainable practices in manufacturing solar trackers. For example, Nextracker has introduced a solar tracker system with a carbon footprint up to 35% lower than traditional trackers, achieved through the use of recycled steel and electric arc furnace manufacturing processes.
Use Cases
- Utility-Scale Solar Power Plants: Single-axis solar trackers are predominantly employed in utility-scale solar power plants to enhance energy production. These trackers adjust the orientation of solar panels to follow the sun’s path from east to west, optimizing the angle of incidence and thereby increasing the system’s energy yield. On average, the integration of single-axis trackers can boost energy production by approximately 25% compared to fixed-tilt systems. This improvement translates to a more efficient use of land and resources, making solar energy generation more cost-effective.
- Agrivoltaic Systems: In agrivoltaic applications, single-axis trackers are utilized to simultaneously produce solar energy and support agricultural activities. By adjusting the tilt of solar panels, these trackers can provide partial shading to crops, which can be beneficial in hot climates by reducing water evaporation and protecting plants from extreme temperatures. This dual-use of land enhances the economic viability of solar projects and supports sustainable farming practices.
- Commercial and Industrial Rooftop Installations: For commercial and industrial facilities with rooftop space, single-axis trackers can be installed to maximize solar energy capture. These systems are particularly advantageous in regions with high solar insolation, as they allow for greater energy production without requiring additional land area. The increased energy output can lead to significant cost savings on electricity bills and contribute to the company’s sustainability goals .
- Remote and Off-Grid Power Systems: In remote or off-grid locations, where access to the main power grid is limited, single-axis trackers can be deployed to ensure a reliable and efficient power supply. By optimizing the angle of solar panels throughout the day, these trackers help maintain consistent energy generation, which is crucial for powering essential services and infrastructure in isolated areas.
- Integration with Bifacial Solar Panels: When paired with bifacial solar panels, which capture sunlight on both the front and rear surfaces, single-axis trackers can further enhance energy yield. The combination of tracking and bifacial technology allows for increased light capture, especially from reflected sunlight on the ground, leading to a reduction in the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) by up to 16% compared to conventional monofacial systems.
Major Challenges
- Wind-Induced Structural Failures: Single-axis trackers are susceptible to wind-induced torsional instability, particularly when panels are stowed flat or near-flat. Studies have indicated that such configurations can lead to dynamic instability under wind speeds as low as 40 m/s, resulting in potential structural failures. This vulnerability necessitates robust design considerations to mitigate wind-related risks.
- Increased Land Use Requirements: The deployment of single-axis trackers typically requires more land area compared to fixed-tilt systems. This is due to the need for greater inter-row spacing to prevent shading between panels as they track the sun’s movement. Consequently, the land area required for a desired power output increases by approximately 10% for single-axis trackers. This additional land requirement can lead to higher land acquisition costs and potential land use conflicts.
- Maintenance and Operational Costs: While single-axis trackers can increase energy production, they also introduce additional maintenance and operational costs. The complexity of moving parts and the need for regular adjustments can lead to higher maintenance requirements compared to fixed-tilt systems. These increased costs can affect the overall economic viability of solar projects, especially in regions where labor and service costs are high.
- Terrain Adaptability Issues: Single-axis trackers are designed to follow the sun’s movement along a single axis, typically from east to west. However, in regions with uneven or sloped terrains, the performance of these trackers can be compromised. The need for extensive grading to level the land can increase installation costs and time. In some cases, terrain-following trackers are employed to reduce the need for grading, but these systems require careful design to ensure optimal performance.
- Shading and Interference: The movement of panels in single-axis trackers can lead to shading of adjacent panels, particularly during certain times of the day when the sun’s angle is low. This shading can reduce the overall energy output of the system. To mitigate this, careful planning of panel spacing and orientation is required, which can complicate the design and increase costs.
Growth Opportunities
- Rising Demand for Renewable Energy: The global emphasis on reducing carbon emissions has led to increased investments in renewable energy sources. Single-axis trackers, by improving the efficiency of solar panels, play a crucial role in this transition. Their ability to increase energy output by up to 25% compared to fixed-tilt systems makes them an attractive option for utility-scale solar projects.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in tracker technology, such as the integration of bifacial solar modules, have enhanced the performance of single-axis trackers. Bifacial modules capture sunlight on both sides, and when combined with single-axis trackers, they can reduce the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) by 16% compared to conventional systems.
- Government Incentives and Policies: Supportive government policies and incentives worldwide are accelerating the adoption of solar technologies. For instance, tax credits and subsidies in various countries are making investments in solar infrastructure more financially viable, thereby boosting the demand for efficient tracking systems.
Key Players Analysis
- Arctech Solar
- Array Technologies
- Canadian Solar
- Valmont Industries, Inc.
- DEGERenergie
- First Solar
- Fronius International
- Hanwha Group
- JA Solar
- JinkoSolar
- Kyocera Corporation
- Nextracker
- PV Hardware
- Soltec Power Holdings
- SunPower Corporation
- Trina Solar
Recent Developments
In 2023, Arctech Solar significantly expanded its global footprint in the single-axis solar PV tracker sector. Notably, the company secured a 2.3 GW contract to supply its SkyLine II trackers for ACWA Power’s Haden project in Saudi Arabia, enhancing its presence in the Middle East and Africa region . Additionally, Arctech commenced shipments for a 320 MW project in Uzbekistan, showcasing the rapid deployment capabilities of its SkyLine II system . In 2024, Arctech continued its growth trajectory by entering the Israeli market with an 11.5 MW SkyLine II project . These strategic projects underscore Arctech’s commitment to delivering advanced solar tracking solutions across diverse geographies.
In 2023, Array Technologies solidified its leadership in the single-axis solar tracker market through several high-profile projects. The company supplied nearly 1 GW of its DuraTrack® trackers for the Gemini project in Nevada, poised to be the largest operational solar-plus-storage facility in the U.S. upon completion . Array also secured a contract to provide trackers for an over 750 MWdc solar project in Ohio, demonstrating its capacity to support large-scale installations . Furthermore, Array’s collaboration with RP Construction Services surpassed 6 GW of deployed solar power, highlighting its extensive reach in the U.S. market . These milestones reflect Array’s ongoing commitment to advancing solar energy infrastructure nationwide.
In 2023, Canadian Solar advanced its role in the single-axis solar PV tracker sector by supplying modules for the 43.1 MW NC31 project in North Carolina, utilizing single-axis trackers to enhance energy yield. The company also collaborated with Flow Power in 2024 to install innovative anti-hail solar tracking systems in South Australia, aiming to improve durability and performance in extreme weather conditions . These initiatives reflect Canadian Solar’s commitment to integrating advanced tracking technologies to optimize solar energy production across diverse climates.
In 2023, Valmont Industries, through its Valmont Solar division, continued to expand its presence in the single-axis solar PV tracker market. The company has been providing its Convert single-axis trackers for over 15 years, known for their durability and ease of installation . In 2024, Valmont introduced the Convert Versa Tracker in Europe, designed for both distributed and large-scale PV projects, demonstrating its commitment to innovation in solar tracking solutions . These developments underscore Valmont’s ongoing efforts to enhance solar energy efficiency through advanced tracking technologies.
In 2023, DEGERenergie expanded its single-axis solar PV tracker installations, notably deploying 11 DEGER S100-PF-SR units in a 1.5 MW project for Amber Grid in Lithuania, enhancing renewable energy infrastructure in the region . The company also introduced the DEGER S100-AG-DR in 2024, a single-axis tracker with a 120 m² module surface area, tailored for agri-photovoltaic applications . These developments underscore DEGERenergie’s commitment to advancing solar tracking technology and supporting diverse energy projects across Europe.
In 2023, First Solar introduced its first bifacial thin-film cadmium telluride (CdTe) solar module, enhancing compatibility with single-axis trackers and improving energy yield . The company maintained robust capital expenditures to expand manufacturing facilities in Alabama and Louisiana, positioning itself for increased production capacity in 2024 . These strategic initiatives reflect First Solar’s dedication to innovation and its role in advancing solar tracking technologies.
In 2023, Fronius International focused on enhancing its role in the solar energy sector by producing a record number of inverters in its 30-year history, emphasizing its commitment to renewable energy solutions . While Fronius does not manufacture single-axis solar PV trackers, its inverters are integral to solar installations that utilize such tracking systems, ensuring optimized energy conversion and system efficiency. In 2024, Fronius continued to position itself as a holistic solution provider in renewable energy, highlighting its durable products and responsible resource use at Intersolar 2024.
In 2023, Hanwha Group, through its affiliate 174 Power Global, collaborated with NEXTracker to supply single-axis solar trackers for a 3.4 GW U.S. solar portfolio, marking a significant expansion in utility-scale solar projects . This partnership underscores Hanwha’s strategic investment in advanced solar tracking technologies to enhance energy yield. In 2024, Hanwha Qcells, a subsidiary of Hanwha Group, maintained its leading market share in the solar industry, focusing on developing next-generation perovskite tandem cell technology, which complements the efficiency gains from single-axis trackers.
In 2023, JA Solar enhanced its involvement in the single-axis solar PV tracker sector by supplying high-efficiency modules for various utility-scale projects, including a 2.2 MW solar tracker farm in South Burlington, Vermont, in collaboration with AllEarth Renewables. This project utilized single-axis trackers to maximize energy output. In 2024, JA Solar continued to support the integration of its modules with advanced tracking systems, focusing on improving energy yields and system performance across diverse geographies. These initiatives underscore JA Solar’s commitment to advancing solar tracking technologies and expanding its global footprint.
In 2023, JinkoSolar advanced its role in the single-axis solar PV tracker sector by supplying its high-efficiency Tiger Neo modules for various utility-scale projects, particularly in the Middle East and Africa regions. These modules were integrated with single-axis tracking systems to optimize energy production. In 2024, JinkoSolar achieved a significant milestone by developing perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells with a record 33.24% efficiency, enhancing compatibility with tracking systems and improving overall system performance. These developments highlight JinkoSolar’s commitment to innovation and its strategic focus on enhancing solar energy solutions through advanced tracking technologies.
In 2023, Kyocera Corporation continued its focus on solar module production, supplying high-efficiency panels compatible with single-axis trackers for various utility-scale projects. While Kyocera does not manufacture trackers, its modules are often integrated into systems utilizing such technology to optimize energy yield. In 2024, Kyocera maintained its commitment to renewable energy solutions, emphasizing the durability and performance of its solar modules in diverse environmental conditions. These efforts underscore Kyocera’s role in supporting solar tracking applications through reliable photovoltaic products.
In 2023, Nextracker solidified its leadership in the single-axis solar PV tracker market by deploying its NX Horizon™ system across over 90 GW of solar capacity worldwide. The company introduced the NX Horizon-XTR™, designed for challenging terrains, and launched a low-carbon tracker solution with up to 35% reduced carbon footprint. In 2024, Nextracker expanded its manufacturing capabilities by opening a second solar tracker plant in Las Vegas, enhancing its capacity to support over 2 GW of new solar power annually. These initiatives highlight Nextracker’s commitment to innovation and sustainability in solar tracking technology.
In 2023, PV Hardware (PVH) achieved a significant milestone by surpassing 28 GW of solar tracker installations globally, solidifying its position as the third-largest solar tracker manufacturer worldwide. The company introduced the Monoline 3H, a wireless, self-powered single-axis tracker designed for hilly terrains and irregular plots, enhancing adaptability and reducing installation complexities. In 2024, PVH continued its innovation trajectory with the launch of the Axone Duo Infinity, a dual-row tracker system optimized for bifacial modules, aiming to maximize energy yield and land use efficiency. These advancements underscore PVH’s commitment to delivering versatile and efficient solar tracking solutions across diverse geographies.
In 2023, Soltec Power Holdings experienced a remarkable 179% year-over-year growth in solar tracker supply, delivering 813 MW compared to 291 MW in the previous year. This surge was driven by the widespread adoption of its SFOne single-axis tracker, known for its adaptability to various terrains. To further enhance its offerings, Soltec introduced the 4×4 foundation option for the SFOne in 2024, expanding slope tolerance and reducing land preparation requirements. These developments highlight Soltec’s dedication to providing innovative and flexible solar tracking solutions that meet the evolving needs of the renewable energy sector.
In 2023, SunPower Corporation advanced its position in the single-axis solar PV tracker sector by deploying its T0 Tracker system in various utility-scale projects. The T0 Tracker, designed to minimize shading and optimize land use, enables installations to require 20% less land than conventional fixed-tilt systems. In 2024, SunPower continued to enhance its tracker technology, focusing on integrating high-efficiency solar panels with advanced tracking algorithms to maximize energy yield. These efforts underscore SunPower’s commitment to delivering efficient and space-optimized solar tracking solutions.
In 2023, Trina Solar expanded its single-axis solar PV tracker offerings through its TrinaTracker division, launching the Vanguard 2P tracker. This dual-row, single-axis tracker is compatible with large modules up to 685 W and features a multi-motor control system to withstand higher wind loads and reduce tilt angle misalignment. In 2024, Trina Solar continued to enhance its tracker solutions, focusing on intelligent mechanisms and improved synchronization to optimize performance and reduce operational costs. These developments highlight Trina Solar’s dedication to advancing solar tracking technology for diverse environmental conditions.
Conclusion
Single-axis solar PV trackers play a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency and economic viability of solar energy systems across various applications. Their ability to optimize the orientation of solar panels ensures maximum energy capture, making them a valuable component in the transition towards renewable energy solutions. As technology advances and costs decrease, the adoption of single-axis trackers is expected to increase, further driving the growth of the solar energy industry.




