Table of Contents
Overview
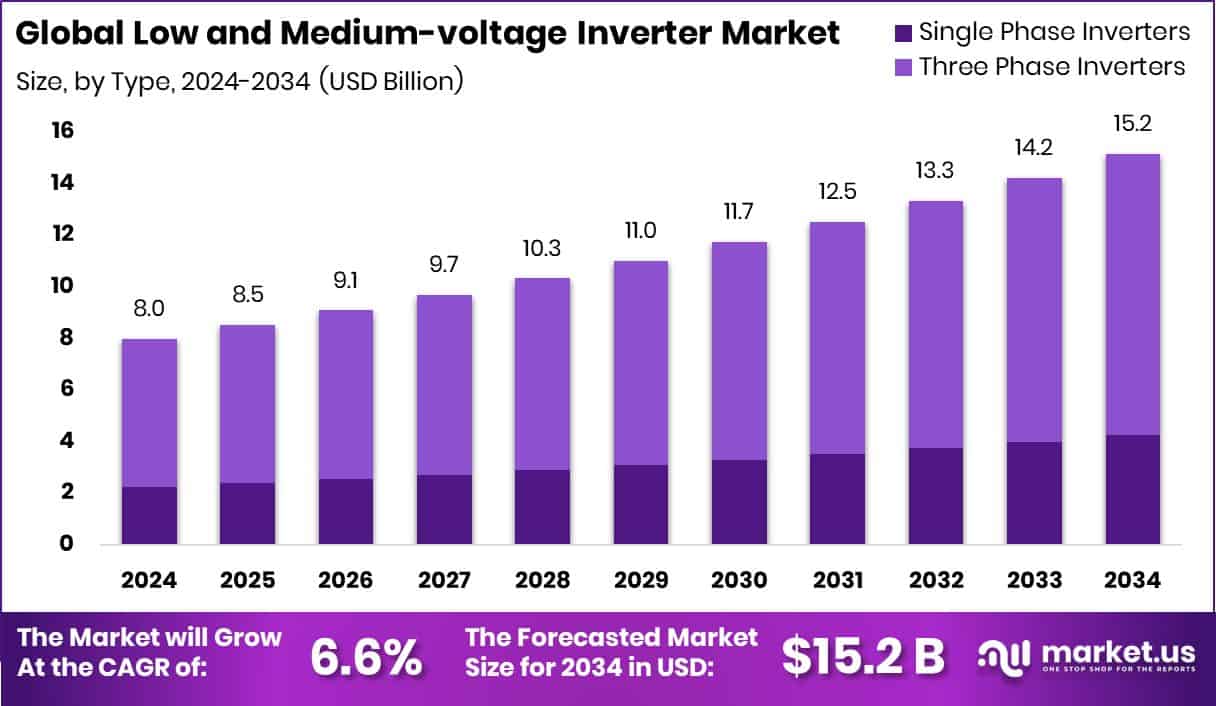
New York, NY – August 08, 2025 – The global Low and Medium-voltage Inverter market is projected to grow from USD 8.0 billion in 2024 to USD 15.2 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 6.6% from 2025 to 2034. These inverters convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) within defined voltage ranges—low-voltage units operate below 1,000 V, while medium-voltage units handle about 1,000 V to 35,000 V. They are widely applied in industrial machinery, renewable energy systems, motor drives, HVAC, and utility-scale grid operations.
Market growth is driven by industrial automation, renewable energy adoption, and modernization of power grids. Rising solar and wind installations are boosting demand for efficient, high-capacity inverters, supported by clean energy policies worldwide. In industrial settings, their use in variable frequency drives helps reduce energy waste, cut operational costs, and improve motor performance, particularly in sectors such as water treatment, mining, and oil & gas.
Opportunities are emerging from transportation electrification and infrastructure expansion in developing regions, including electric vehicle charging networks and rural electrification. Additionally, the rise of smart buildings and decentralized energy systems is creating new deployment avenues in both residential and commercial markets, reinforcing the inverters’ role in enhancing efficiency and supporting sustainable energy transitions.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Low and Medium-voltage Inverter Market is expected to be worth around USD 15.2 billion by 2034, up from USD 8.0 billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.6% from 2025 to 2034.
- Three-phase inverters dominate the Low and Medium-voltage Inverter Market with 72.9% market share.
- Low-voltage inverters (up to 1 MW) lead the market, capturing a 65.4% share.
- Commercial users accounted for 47.5% of the total Low and Medium-voltage inverter market share.
➤ For a deeper understanding, click on the sample report link: https://market.us/report/global-low-and-medium-voltage-inverter-market/request-sample/
Report Scope
| Market Value (2024) | USD 8.0 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 15.2 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 6.6% |
| Segments Covered | By Type (Single Phase Inverters, Three Phase Inverters), By Power Rating (Low Voltage Inverters (up to 1 MW), Medium Voltage Inverters (1 MW to 5 MW)), By End-User (Commercial, Residential, Industrial) |
| Competitive Landscape | ABB, Fuji Electric, Siemens, Schneider Electric, Danfoss, Yaskawa, Delta, Hitachi, LENZE, Nidec |
➤ Directly purchase a copy of the report – https://market.us/purchase-report/?report_id=154600
Key Market Segments
By Type Analysis
In 2024, Three Phase Inverters led the Low and Medium-voltage Inverter market’s By Type segment with a 49.2% share, driven by their extensive use in high-power industrial systems, large motor drives, and grid-connected renewable projects. Favored for their stable, efficient power conversion, they ensure balanced load distribution and high energy output, making them vital in manufacturing, commercial, and energy facilities.
Their compatibility with variable frequency drives and role in achieving energy efficiency targets further boost adoption. Offering enhanced performance, reduced harmonic distortion, and reliable operation under continuous load, three-phase technology is increasingly chosen for complex power systems and demanding grid integration needs.
Industrial expansion and growing renewable energy deployments, especially in emerging regions, are accelerating their uptake. As automation and energy optimization gain priority across energy-intensive sectors, three-phase inverters are expected to retain their leading market position in the coming years.
By Power Rating Analysis
In 2024, Low Voltage Inverters (up to 1 MW) dominated the By Power Rating segment of the Low and Medium-voltage inverter market with a 49.2% share, driven by strong adoption in small to mid-sized industries, commercial buildings, and decentralized renewable systems. Valued for their compact design, cost efficiency, and easy integration into existing networks, they are ideal for moderate energy demand applications where efficiency is essential.
Rising emphasis on energy-saving technologies in light industrial operations and commercial spaces has fueled demand, with these inverters playing a key role in improving motor control, cutting electricity consumption, and ensuring smooth operation in HVAC, pumps, and fans.
The surge in manufacturing automation further supports their growth, as they deliver scalable, reliable, and efficient power conversion. Their versatility across varied energy-conscious applications solidifies their lead in the power rating segment and sustains their position as a preferred choice in efficiency-focused environments.
By End-User Analysis
In 2024, the Commercial sector led the by-end-user segment of the Low and Medium-voltage Inverter Market with a 49.2% share, driven by rising demand for reliable, energy-efficient power conversion in facilities such as malls, offices, hospitals, schools, and data centers. These inverters help optimize power loads, lower energy use, and ensure uninterrupted operations.
Adoption is further fueled by the integration of renewable energy systems like rooftop solar, where inverters convert DC output into usable AC power. They also play a vital role in building automation and energy management, supporting HVAC, elevators, lighting, and backup systems.
The sector’s focus on efficiency and sustainability, coupled with rapid urbanization and expanding commercial infrastructure, continues to strengthen its dominance. As demand for stable, optimized energy solutions grows, the commercial segment is well-positioned to maintain its market leadership.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, Asia-Pacific led the Low and Medium-voltage Inverter Market with 43.6% of global revenue, valued at USD 3.4 billion. This dominance is fueled by rapid industrialization, major infrastructure investments, and expanding renewable energy projects in nations like China, India, and across Southeast Asia. Strong emphasis on energy efficiency and smart manufacturing is further accelerating adoption in both industrial and commercial sectors.
North America is experiencing steady growth through advancements in power electronics and wider integration of smart energy systems, while Europe’s demand is rising with its carbon neutrality goals and clean energy adoption in industry and public infrastructure. The Middle East & Africa are gradually increasing inverter use, particularly in large-scale solar and infrastructure projects aimed at energy diversification.
Latin America is advancing through commercial applications and solar developments, yet Asia-Pacific remains the clear market leader, serving as the primary hub for large-scale power management deployment and future industry growth.
Top Use Cases
Industrial Energy Saving via AC Drives: Replacing steam turbine-driven compressors in a Yunnan (China) steel plant with inverter-fed AC drive systems delivered around 20% annual energy savings, helping cut CO₂ emissions significantly.
DC Microgrids in Data Centers: DC-powered microgrids can deliver up to 200% higher reliability compared to traditional AC setups while reducing conversion stages and complexity. These systems boost uptime in energy-critical facilities like data centers.
Energy-Efficient Smart Factories: Industrial machinery—such as conveyor belts and robotic arms—benefits from DC microgrids powered by inverters. These systems cut regeneration and conversion losses, achieving energy savings of up to 20% in factory automation.
Home Energy Systems with Backup: Hybrid inverters in homes—rated around 10 kW—provide backup power during outages. They seamlessly convert DC from rooftop solar or batteries to AC, enabling automatic switchovers without extra control boxes, simplifying installation, and improving resilience.
Utility-Scale Solar Inverter Use: In utility-scale photovoltaic (PV) projects (9.47 TW across 14,757 simulations), Huawei’s SUN2000‑215KTL‑H3 string inverter held approximately 11% share, delivering ≥ 99.0% efficiency and 200 kW rated active power.
Recent Developments
- In May 2024, Fuji Electric launched its FRENIC-GS series as part of its FY2024 lineup. Built for industrial environments, the series combines a compact form factor with high energy efficiency. It has already been implemented in sectors such as steel manufacturing and harbor crane operations, where maximizing space utilization and optimizing power consumption are essential.
- In May 2024, ABB unveiled an integrated motor-and-inverter solution for electric buses at Busworld Turkey 2024. This system features the debut of the HES580 three-level inverter, paired with the AMXE250 motor. The configuration cuts motor harmonic losses by as much as 75% and motor losses overall by up to 12% compared to conventional two-level inverters—enhancing efficiency, extending motor lifespan, and meeting the demands of intensive transit operations.
Conclusion
Low-voltage and medium-voltage inverters are essential for turning electric energy into the right kind of power needed by machines and industrial systems. The low-voltage inverters are compact and ideal for smaller motors, appliances, and equipment, offering precise control and efficiency in everyday tasks. On the other hand, medium-voltage inverters serve larger systems—like heavy-duty machinery, large pumps, and factory operations—where they help save energy and make big machines run more smoothly. Together, these inverters play a vital role in improving performance, cutting energy waste, and ensuring machines stay reliable—whether it’s for small factory tools or big industrial plants.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





