Table of Contents
Overview
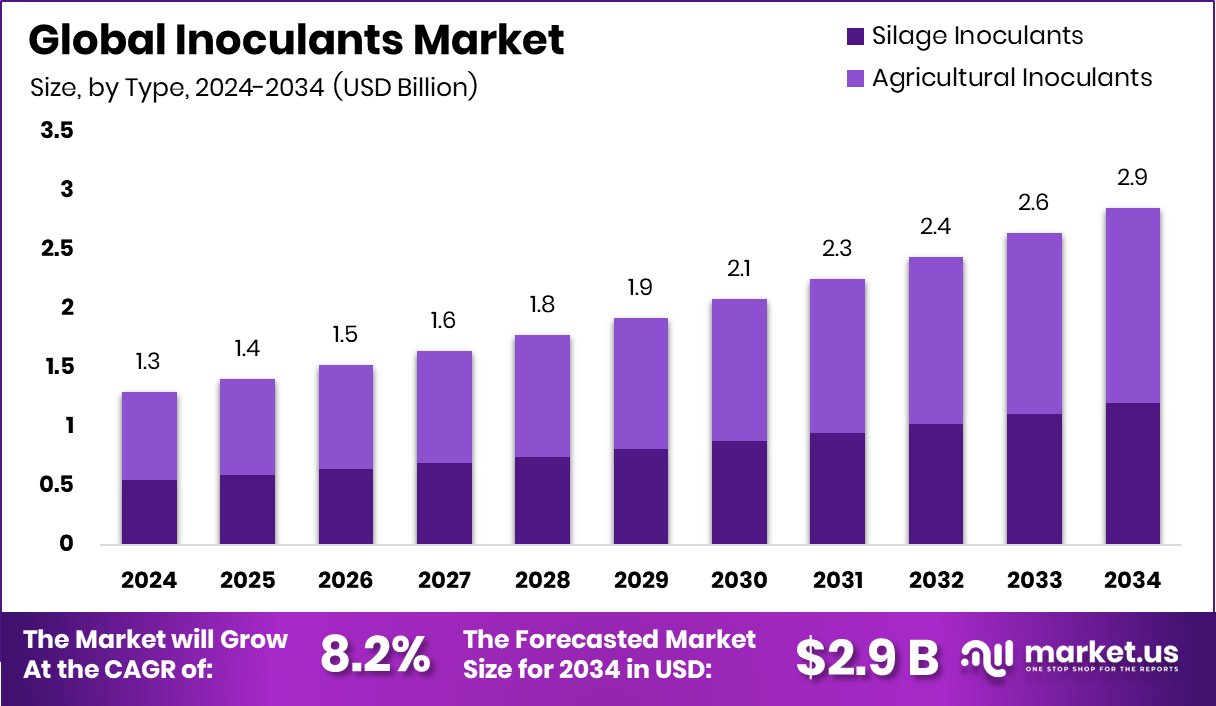
New York, NY – September 26, 2025 – The Global Inoculants Market is on a steady rise, expected to grow from USD 1.3 billion in 2024 to around USD 2.9 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 8.2% between 2025 and 2034. North America remains a key region, accounting for nearly 47.9% of the market, valued at approximately USD 0.6 billion.
Inoculants are microbial formulations made up of bacteria, fungi, or yeasts that are applied to seeds, soil, or plants to support healthy growth. These solutions improve nutrient uptake, enhance soil fertility, and stimulate stronger root systems, making them a vital tool for sustainable agriculture. As farmers worldwide adopt eco-friendly practices and governments encourage greener methods, the demand for inoculants is accelerating.
Notably, companies are scaling up their innovations: NewLeaf Symbiotics raised USD 45 million to expand microbial amendments for row crops; Groundwork BioAg secured USD 11 million to grow its mycorrhizal-based solutions; and Biobest invested USD 570 million to acquire Brazil’s Biotrop, strengthening its foothold in South America. With rising populations and increasing food security concerns, inoculants provide a sustainable pathway to higher yields without compromising soil health, thereby cementing their role in the future of farming.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Inoculants Market is expected to be worth around USD 2.9 billion by 2034, up from USD 1.3 billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.2% from 2025 to 2034.
- Agricultural inoculants lead the inoculants market with 58.4%, reflecting strong adoption in modern farming practices.
- Bacterial segment dominates the inoculants market at 79.2%, showcasing microbes’ efficiency in boosting crop productivity.
- Dry form holds 53.6% share in the inoculants market, driven by easier handling and storage.
- Cereals account for 48.7% of the inoculants market, highlighting their critical role in global agriculture.
- Farmers in North America increasingly adopt inoculants, driving 47.9% regional growth worth USD 0.6 Bn.
➤ Curious about the content? Explore a sample copy of this report – https://market.us/report/inoculants-market/request-sample/
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2024) | USD 1.3 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 2.9 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 8.2% |
| Segments Covered | By Type (Silage Inoculants, Agricultural Inoculants), By Microbe (Fungal, Bacterial), By Form (Dry, Liquid), By Crop Type (Cereals, Oilseeds and Pulses, Fruits and Vegetables, Others) |
| Competitive Landscape | Corteva Agriscience, BASF SE, Bayer AG, Novozymes A/S, Cargill, Incorporated, Archer Daniels Midland Company, Lallemand Inc., Kemin Industries, Inc., Verdesian Life Sciences, BIO-CAT |
➤ Directly purchase a copy of the report – https://market.us/purchase-report/?report_id=157443
Key Market Segments
By Type Analysis
Agricultural inoculants lead the Inoculants Market, commanding a 58.4% share in 2024. Their dominance stems from the increasing reliance on microbial solutions to boost soil fertility, crop productivity, and nutrient uptake in crops like cereals, legumes, and forage.
Farmers are adopting these eco-friendly alternatives to chemical fertilizers to sustain high yields while promoting soil health. The segment’s growth is fueled by rising global food demand, population growth, and the need for resilient farming systems amid changing climates. Advances in microbial research further enhance the effectiveness of agricultural inoculants, tailoring them to diverse agro-climatic zones and solidifying their position as the most widely adopted type.
By Microbe Analysis
The bacterial segment dominates the Inoculants Market with a 79.2% share in 2024, driven by the widespread use of bacteria like rhizobia to enhance soil fertility and plant growth. These inoculants excel in nitrogen fixation, nutrient uptake, and root system development, offering a sustainable alternative to synthetic fertilizers.
Their versatility across crops such as cereals, legumes, and oilseeds, combined with advancements in microbial biotechnology, ensures their reliability in varied soil and climatic conditions. As soil degradation and chemical input costs rise, bacterial inoculants remain a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture, maintaining their market leadership.
By Form Analysis
Dry inoculants hold a 53.6% share of the Inoculants Market in 2024, favored for their ease of use, extended shelf life, and cost-effectiveness. Their compatibility with seed application and minimal storage requirements makes them accessible to both small- and large-scale farmers.
Technological advancements have improved the stability and efficacy of dry inoculants, ensuring consistent delivery of beneficial microbes for nitrogen fixation and root development. As farmers prioritize sustainable, affordable inputs, dry inoculants continue to lead due to their practicality and performance across diverse crop types and environmental conditions.
By Crop Type Analysis
Cereals dominate the Inoculants Market with a 48.7% share in 2024, driven by their role as global staple crops like wheat, maize, rice, and barley. The massive scale of cereal cultivation fuels demand for inoculants, which enhance nitrogen fixation, nutrient availability, and plant resilience, ensuring higher yields and soil fertility. With global population growth increasing pressure on food production, inoculants are critical for sustainable cereal farming. Their ability to improve root development and withstand environmental stresses further cements their importance, making cereals the leading segment in the market.
Regional Analysis
North America leads the Inoculants Market with a 47.9% share, valued at USD 0.6 billion in 2024, driven by advanced farming practices, high adoption of sustainable solutions, and supportive government policies. The U.S. and Canada spearhead the shift toward biological inputs for row crops and forage.
Europe follows, propelled by stringent environmental regulations, while the Asia Pacific sees rapid growth due to population-driven food security needs. Latin America’s commercial farming expansion and the Middle East & Africa’s focus on addressing soil fertility challenges contribute to global demand. North America’s innovation and infrastructure set the standard for sustainable agriculture, reinforcing its market dominance.
Top Use Cases
- Nitrogen Fixation in Legumes: Farmers apply bacterial inoculants like rhizobia to legume seeds, such as soybeans or peas, before planting. These helpful microbes form root nodules that pull nitrogen from the air and turn it into a form plants can use. This natural process boosts plant growth without heavy chemical fertilizers, cuts costs, and keeps soil healthy for future crops, making farming more sustainable and productive.
- Phosphorus Solubilization for Better Uptake: In soils low on available phosphorus, farmers use inoculants with phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on crops like maize or wheat. The microbes release locked-up phosphorus through acids and enzymes, helping roots absorb this key nutrient easily. This leads to stronger plants, higher yields, and less need for pricey rock phosphate, supporting eco-friendly practices in nutrient-poor fields.
- Biocontrol Against Soil Pathogens: Growers treat seeds or soil with fungal inoculants like Trichoderma to fight root diseases in vegetables or cereals. These microbes compete with harmful pathogens, produce antibiotics, and trigger plant defenses, reducing crop losses from rot or wilt. It’s a safe, natural shield that lowers pesticide use and promotes healthier fields without harsh chemicals.
- Drought Stress Tolerance in Dry Areas: In water-scarce regions, inoculants with plant growth-promoting bacteria are added to crops like rice or barley to build resilience. They improve root growth, retain soil moisture, and release stress-fighting hormones, helping plants survive dry spells. This approach enhances yields in tough climates, aids small farmers, and fits into climate-smart farming strategies.
- Silage Preservation for Livestock Feed: Dairy and beef producers mix bacterial inoculants into chopped forage during ensiling to speed up fermentation. These microbes convert sugars to acids, dropping pH quickly to prevent spoilage and nutrient loss. The result is tastier, more nutritious feed that lasts longer, reduces waste, and supports efficient animal husbandry with better milk or meat output.
Recent Developments
1. Corteva Agriscience
Corteva Agriscience is advancing inoculants through its Optinyte technology, focusing on biological nitrogen fixation for soybeans and other legumes. Recent developments highlight improved strain selection and coating processes to enhance yield and consistency. Their research integrates these biologics with traditional seed treatments, offering a holistic seed-applied solution for farmers seeking to optimize nutrient use efficiency and reduce environmental impact as part of their sustainable agriculture portfolio.
2. BASF SE
BASF’s recent inoculant developments are channeled through its BASF Agricultural Solutions segment. They focus on novel microbial strains for the Vivient brand, particularly for corn and soybeans. Their research aims to enhance phosphate solubility and nitrogen fixation, working synergistically with chemical inputs. A key initiative is developing combination products that pair effective inoculants with fungicide and insecticide seed treatments to simplify application and improve early plant vigor.
3. Bayer AG
Bayer AG is investing heavily in its BioRise biologicals portfolio, which includes next-generation inoculants. A significant recent development is the use of data science and microbiome research to identify and design more effective, stress-resilient microbial combinations. Their focus extends beyond legumes to cover crops like corn and wheat, aiming to unlock nutrients and improve soil health, aligning with their broader Carbon Initiative and sustainability goals.
4. Novozymes A/S
As a world leader in biological solutions, Novozymes consistently launches new microbial strains. A key recent development is the expansion of their TagTeam and HiStick families with strains offering tolerance to certain seed treatment chemicals. They also emphasize microorganisms that perform under abiotic stresses like drought. Their strategy involves strong partnerships with seed companies to co-develop and integrate advanced inoculant technologies directly onto seed for ease of use.
5. Cargill, Incorporated
While not a direct inoculant manufacturer, Cargill is actively developing its animal feed and sustainability segments, which involve microbial applications. Recent developments include investing in and partnering with startups specializing in methane-reducing feed inoculants for livestock. These probiotics aim to alter the gut microbiome of animals, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This represents a crucial application of inoculant technology in agriculture’s value chain beyond crop production.
Conclusion
Inoculants as a game-changer for modern farming. They offer a smart way to nurture soil life, cut down on harmful chemicals, and build tougher crops against weather woes and pests. With farmers worldwide chasing greener methods, these microbial helpers promise steady growth, healthier lands, and reliable harvests. Embracing them fully could reshape how we feed the planet sustainably, blending nature’s power with practical gains for everyone in the chain.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





