Table of Contents
Overview
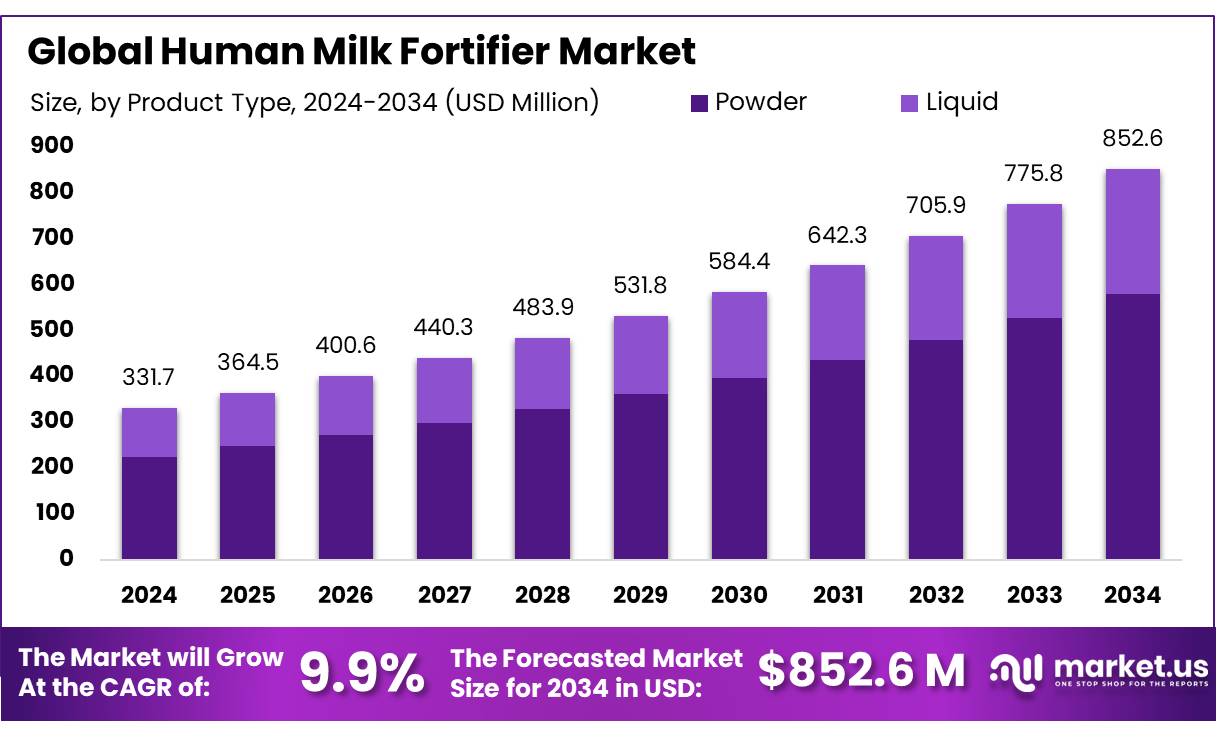
New York, NY – August 12, 2025 – The Global Human Milk Fortifier (HMF) Market is projected to reach approximately USD 852.6 million by 2034, up from USD 331.7 million in 2024, registering a robust CAGR of 9.9% from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America led the market, accounting for over 47.2% of global revenue, valued at USD 156.5 million.
Human milk fortifier concentrates are specialized nutritional supplements added to a mother’s own milk or donor milk to meet the elevated nutrient demands of preterm and very low birth-weight infants. Unlike standard breast milk, HMF formulations enhance protein, calcium, phosphorus, vitamins, and other micronutrients, enabling improved growth rates—such as an average weight gain of 2.82 g/kg/day and length increases of around 0.21 cm/week in very preterm newborns.
While adoption is widespread in advanced healthcare systems, countries like India still face limited uptake due to factors such as high costs, feed intolerance concerns, and logistical challenges. Clinical research continues to validate the benefits of HMF use. A WHO review of ten trials involving 635 preterm infants found that fortified human milk increased weight gain by an average of 1.81 g/kg/day, with statistically significant improvements in length and head circumference, even in low- and middle-income settings.
Although direct government programs for HMF adoption are not yet established, broader food fortification policies set an encouraging precedent. In India, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) regulates nutrient enrichment under the Food Fortification Regulations, while the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) has rolled out large-scale vitamin A and D milk fortification programs, reaching over 121 million people daily.
These initiatives signal growing recognition of early-life micronutrient needs, potentially paving the way for neonatal guidelines to include fortified breast-milk supplements. Further growth could be driven by expanding donor milk banking through government support, public-private partnerships, and emerging technologies such as point-of-care osmotic concentration devices, which can boost nutrient density by more than 30% in NICU settings without reliance on powdered fortifiers.
Key Takeaways
- Human Milk Fortifier Market size is expected to be worth around USD 852.6 Million by 2034, from USD 331.7 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.9%.
- Powder held a dominant market position in the Human Milk Fortifier Market, capturing more than a 67.9% share.
- Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs) held a dominant market position in the Human Milk Fortifier Market, capturing more than a 56.1% share.
- Hospital Supply Chains held a dominant market position in the Human Milk Fortifier Market, capturing more than a 38.4% share.
- North America emerged as the leading region in the global Human Milk Fortifier Market, accounting for a substantial 47.2% share, which translated to a market value of approximately USD 156.5 million.
➤ Curious about the content? Explore a sample copy of this report – https://market.us/report/human-milk-fortifier-market/request-sample/
Report Scope
| Market Value (2024) | USD 331.7 Million |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 852.6 Million |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 9.9% |
| Segments Covered | By Product Type (Powder, Liquid), By End User (Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs), Hospitals and Clinics, Home Care Settings, Research Institutions, Others), By Distribution Channel (Hospital Supply Chains, Direct Sales, Online Retail, Pharmacies, Others) |
| Competitive Landscape | Abbott, MeadJohnson, NeoLacta Lifesciences Pvt Ltd, Nestle SA, Prolacta Bioscience Inc, NeoKare Nutrition Ltd, Danone SA, Neolac Inc |
➤ Directly purchase a copy of the report – https://market.us/purchase-report/?report_id=154133
Key Market Segments
By Product Type Analysis
In 2024, powder-form human milk fortifiers dominated the market, securing over 67.9% of the global share. Their popularity stems from extended shelf life, ease of handling, and seamless compatibility with hospital feeding protocols. In neonatal intensive care units (NICUs), powdered fortifiers are the preferred choice due to their cost-effectiveness, straightforward storage, and ability to support individualized feeding plans.
This format allows flexible dosage adjustments tailored to an infant’s weight and medical needs, enabling precise nutritional support for preterm and low birth weight babies. Furthermore, powder production and distribution costs are lower compared to liquid variants, making it ideal for large-scale institutional supply. Powder-form fortifiers are expected to retain their lead, backed by strong adoption in clinical environments and the consistent preference of healthcare professionals for their practicality and efficiency.
By End User Analysis
Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs) accounted for more than 56.1% of the human milk fortifier market in 2024, driven by the rising incidence of preterm births and the critical need for specialized hospital-based nutrition. In these settings, fortifiers are essential to help premature and low birth weight infants achieve healthy growth and reduce complications.
NICUs often adopt exclusive human milk feeding protocols, integrating fortifiers as a standard component of care. This strong clinical foundation positions hospitals as the primary end-user segment. With global healthcare systems investing more in neonatal care and survival outcomes, NICUs are set to maintain their market leadership in 2025.
By Distribution Channel Analysis
Hospital supply chains led the distribution landscape in 2024, representing 38.4% of total market share. Centralized procurement, bulk purchasing, and adherence to strict quality and safety standards make hospitals the most reliable channel for human milk fortifier distribution, particularly in facilities with NICUs.
By ensuring continuous product availability, regulatory compliance, and streamlined logistics, hospital supply networks remain the most efficient route for clinical use. This dominance is expected to persist in 2025, supported by rising hospital deliveries, growing NICU admissions, and expanding healthcare infrastructure worldwide.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America led the global human milk fortifier market with a 47.2% share, generating USD 156.5 million in revenue. This leadership is underpinned by advanced healthcare systems, high NICU availability, and a strong emphasis on preterm infant nutrition.
The U.S. remains the primary growth driver, with high hospital birth rates and well-established feeding protocols that integrate fortifiers into neonatal care. Government initiatives, such as the Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) program, further encourage the use of fortifiers for eligible families.
The CDC reports that roughly 1 in 10 U.S. infants is born prematurely, reinforcing the need for specialized nutrition. The presence of leading pediatric hospitals, favorable reimbursement frameworks, and ongoing neonatal research ensures that North America will likely retain its top position through 2025 and beyond.
Top Use Cases
- Preterm Growth Boost: Hospitals use HMF to enrich breast milk with extra protein, minerals, and vitamins so premature babies can grow more effectively. This fortified nutrition helps improve weight gain, bone development, and overall health in the critical early days after birth.
- Tailored NICU Care: Neonatal Intensive Care Units personalize HMF dosages based on each infant’s weight and medical needs. This customized approach ensures babies at different developmental stages receive the right concentration to support their rapid growth and recovery.
- Donor Milk Enhancement: Human milk banks supply donor milk that may lack specific nutrients needed by preterm infants. Adding HMF to donor milk ensures that these babies receive complete nutrition, bridging gaps caused by the limited availability of their own mother’s milk.
- Post-Discharge Nutritional Support: Some medically supervised infants continue using HMF at home after leaving the hospital. This support helps maintain growth momentum and ensures nutrient needs are met until the baby reaches full feeding capacity.
- Improved Feeding Tolerance: For infants who struggle with feeding intolerance or previous digestive issues, newer HMF formulations, especially liquid or optimized mixes, reduce discomfort and help infants achieve steady growth without increasing risks of feeding complications.
Recent Developments
1. Abbott
Abbott has advanced its Similac Human Milk Fortifier with HMO (Human Milk Oligosaccharides) to support preterm infants’ immune systems. Their concentrated liquid fortifier is designed to blend seamlessly with breast milk, improving nutrient absorption. Abbott continues research on microbiome benefits and has introduced ready-to-use formats for NICU convenience. Recent studies highlight reduced feeding intolerance.
2. MeadJohnson (Reckitt)
MeadJohnson, under Reckitt, offers Enfamil Human Milk Fortifier, focusing on hydrolyzed proteins for easier digestion in preterm infants. Recent updates include a plant-based DHA source and improved mineral bioavailability. They emphasize reducing necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) risks. Reckitt has also invested in global HMF accessibility programs.
3. NeoLacta Lifesciences
NeoLacta, an India-based leader, launched NeoLacta Forte, the first lyophilized (freeze-dried) human milk-derived fortifier in Asia. Their product retains bioactive components, reducing cow’s milk protein risks. Recent expansions include partnerships with neonatal ICUs for safer preterm nutrition. They focus on donor milk-based fortifiers as an alternative to bovine options.
4. Nestlé SA
Nestlé’s Gerber Good Start Human Milk Fortifier incorporates probiotics to support gut health in preemies. Recent innovations include a low-osmolality formula to minimize digestive stress. Nestlé also emphasizes sustainable sourcing and has expanded HMF availability in emerging markets. Clinical trials focus on neurodevelopmental benefits.
5. Prolacta Bioscience
Prolacta leads in 100% human milk-based fortifiers, with recent FDA-reviewed studies showing lower mortality and NEC rates in extremely preterm infants. Their ProForta range offers higher caloric density. Prolacta has expanded production capacity to meet rising NICU demand and advocates for exclusive human milk diets.
Conclusion
Human Milk Fortifiers are key tools in neonatal nutrition, especially for preterm or medically fragile infants who require more than standard breast milk can provide. Across clinical settings from NICUs to home care, HMF supports tailored nutrition, growth catch-up, and improved tolerability. As healthcare systems strengthen and neonatal survival rises, the role of HMF in delivering precise, safe, and efficient nutritional support continues to expand, reinforcing its importance in early-life care.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





