Table of Contents
Introduction
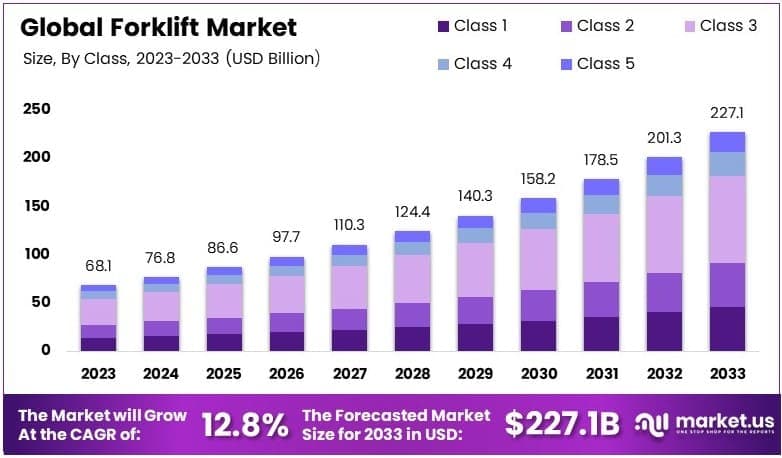
The Global Forklift Market is projected to reach a valuation of USD 227.1 billion by 2033, up from USD 68.1 billion in 2023, reflecting a robust CAGR of 12.8% over the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
A forklift is a powered industrial truck used primarily for lifting, transporting, and stacking materials across various industries. Equipped with two prongs (or forks) at the front, forklifts are integral to material handling in warehouses, construction sites, logistics centers, and manufacturing facilities. Their versatility, ranging from counterbalance forklifts to reach trucks, ensures operational efficiency in moving heavy loads.
The forklift market encompasses the global production, distribution, and sale of forklifts and related services. It includes a wide array of products segmented by power source (electric, internal combustion) and design (counterbalance, warehouse-specific models). This market serves industries such as retail, automotive, construction, and e-commerce, reflecting its broad applicability. The demand for forklifts is a barometer of industrial growth and economic activity, highlighting its critical role in supply chain operations.
Several factors are driving the forklift market’s growth. Rapid industrialization, expansion in e-commerce logistics, and the rising need for efficient warehouse management are primary contributors. The adoption of automation and the integration of smart technologies, like IoT-enabled forklifts, are enhancing operational efficiency, further boosting demand. Additionally, government initiatives to support infrastructure development and industrial investments contribute significantly to the market’s expansion.
The demand for forklifts is witnessing a substantial shift toward electric models, driven by a growing emphasis on sustainability and emission regulations. The rise in warehousing needs due to surging e-commerce activity is another key driver, with companies focusing on optimizing storage and retrieval processes. Moreover, sectors like construction and automotive heavily rely on forklifts to streamline material handling, ensuring consistent demand.
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America present immense opportunities for growth, fueled by urbanization and infrastructure development. The transition to electric forklifts opens avenues for innovation in battery technologies and charging infrastructure. Furthermore, the integration of advanced features, such as autonomous forklifts and AI-driven fleet management, offers manufacturers a chance to differentiate their products in a competitive landscape. These trends suggest that the forklift market is poised for significant advancements, making it a pivotal segment in the material handling industry.
Key Takeaways
- The global forklift market was valued at USD 68.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 227.1 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.8%.
- In 2023, Class III forklifts accounted for 39.7% of the type segment, owing to their adaptability in a wide range of warehouse operations.
- The electric power source segment led the market with a share of 66.5%, driven by the growing preference for sustainable and energy-efficient solutions.
- The retail and wholesale application segment dominated in 2023, emphasizing the essential role forklifts play in modern supply chain management.
- The Asia-Pacific region emerged as the leader, capturing 37.0% of the market, fueled by the rapid expansion of logistics and manufacturing activities in the region.
Forklift Statistics
- A forklift truck can weigh up to 20,000 pounds, much heavier than the typical automobile (3,000 pounds).
- Average forklift weight is over 9,000 pounds.
- Forklifts typically operate at speeds of 18 miles per hour.
- Autonomous and semi-autonomous forklifts are projected to make up 30% of new sales by 2030.
- Europe’s strict emissions rules are driving electric forklift adoption at a rate of 9.5% annually.
- Forklifts are essential to 80% of global supply chain operations.
- Modern electric forklifts use 30% less energy compared to models from a decade ago.
- E-commerce and logistics sectors contribute 40% of forklift demand.
- Manufacturing is the largest end-user, accounting for 35% of total forklift consumption.
- Around 55% of small to medium businesses prefer leasing forklifts over purchasing.
- Forklift and industrial truck accidents result in 34,900 injuries annually.
- 90% of forklift trucks experience accidents during their lifespan.
- Better training policies could prevent 70% of forklift injuries.
- Fatal forklift accidents occur about 87 times per year on average.
- 42% of fatal forklift accidents involve crushing during vehicle tip-overs.
- 36% of forklift fatalities involve pedestrians.
- 30% of forklift accidents happen in warehouses.
- Manufacturing accounts for 42.5% of forklift fatalities, followed by construction at 23.8%.
- Wholesale operations contribute to 12.5% of fatal forklift accidents.
- Forklift overturns are responsible for 25% of all forklift deaths.
- Workers aged 25 to 34 report the highest injury rates, with 1,700 non-fatal injuries annually.
- Forklift-related injuries lead to an average of 18 days off work.
- 17% of forklift accidents involve workers struck by materials.
- Long work shifts (12 hours) increase injury risk by 37%.
- Proper training improves forklift operator performance by over 60%.
- Forklift accidents involving crushing of workers occur in 11% of cases.
- By 2028, the number of industrial truck and tractor operators is expected to grow from 615,000 to 642,000.
Emerging Trends
- Shift to Electric and Hydrogen Fuel Cell Forklifts: There’s a notable transition from internal combustion engine (ICE) forklifts to electric and hydrogen fuel cell alternatives. This shift is propelled by environmental regulations and the pursuit of operational efficiency. Electric forklifts, powered by lithium-ion batteries, offer reduced emissions and lower operating costs. Hydrogen fuel cell forklifts provide rapid refueling and consistent performance in various environments, including refrigerated warehouses. As of 2024, approximately 50,000 hydrogen forklifts are in operation worldwide, predominantly in the U.S.
- Integration of Automation and Advanced Technologies: The adoption of automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies is enhancing forklift operations. Features such as obstacle detection systems, automatic braking, and proximity sensors are improving safety and efficiency. These advancements reduce reliance on manual labor and align with the industry’s move towards smart manufacturing and logistics.
- Growth in E-commerce Driving Demand: The rapid expansion of e-commerce has led to increased demand for efficient material handling solutions. Warehouses and distribution centers are investing in forklifts to manage higher volumes of goods, necessitating equipment that can operate effectively in high-density storage environments.
- Emphasis on Sustainability and Environmental Compliance: Companies are prioritizing eco-friendly practices, leading to a preference for forklifts with lower emissions and energy consumption. This trend is influenced by stringent environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals, encouraging the adoption of electric and hydrogen-powered forklifts.
- Advancements in Battery Technology: Developments in battery technology, particularly lithium-ion batteries, are enhancing forklift performance. These batteries offer longer lifespans, shorter charging times, and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, making them increasingly popular in modern forklift applications.
Top Use Cases
- Warehousing and Inventory Management: Forklifts are widely used to move, stack, and organize goods in warehouses. They help streamline operations in facilities handling large volumes of goods, improving productivity by reducing manual handling efforts. For instance, forklifts can lift pallets weighing up to 5,000 kg, depending on the model, to shelves as high as 10 meters.
- Manufacturing and Production Facilities: In manufacturing plants, forklifts transport raw materials to production lines and shift finished goods to storage or shipping areas. This reduces downtime and ensures a smooth production flow. Many factories rely on forklifts with high load capacities for handling machinery parts and bulk materials efficiently.
- Construction and Heavy Material Handling: Forklifts are used on construction sites to transport heavy loads, such as steel beams, bricks, and concrete. Rough-terrain forklifts are particularly suited for outdoor use, navigating uneven surfaces while carrying loads exceeding 4,000 kg.
- Retail and Large-Scale Stores: Retailers with large inventories, such as home improvement stores, use forklifts to move goods from backrooms to the shop floor. They are also indispensable for unloading deliveries and restocking shelves in bulk. Forklifts with compact designs are preferred for maneuvering in tight spaces commonly found in retail settings.
- Port and Dock Operations: In ports and docks, forklifts are vital for unloading cargo from ships and transferring containers to storage areas. They handle a wide range of goods, from standard pallets to oversized containers, ensuring smooth port operations. Forklifts in this sector often have reinforced structures to manage frequent heavy-duty use.
Major Challenges
- High Initial Investment Costs: Acquiring forklifts, especially advanced models with electric or hydrogen fuel cell technology, requires substantial capital. For instance, electric forklifts can cost 20% more than their internal combustion engine counterparts, posing financial hurdles for small and medium-sized enterprises.
- Workforce Safety Concerns: Forklift-related accidents remain a critical issue. In New South Wales, Australia, at least ten fatalities occurred over five years due to forklift incidents, highlighting the need for improved safety protocols and training.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global supply chain challenges, such as those experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic, have led to delays in forklift production and delivery. In 2022, shipment volumes declined by 12.4% due to decreased demand in key markets like China.
- Maintenance and Operational Downtime: Regular maintenance is essential to prevent operational disruptions. Unexpected breakdowns can lead to significant downtime, affecting productivity and incurring additional costs for repairs and replacements.
- Environmental Regulations Compliance: Stringent environmental laws require manufacturers to develop eco-friendly forklifts. Transitioning to electric models involves challenges such as establishing charging infrastructure and managing battery disposal, which can be complex and costly.
Top Opportunities
- Expansion of E-commerce and Warehousing: The rapid growth of online retail has led to increased demand for efficient material handling solutions in warehouses and distribution centers. This surge necessitates advanced forklifts capable of managing high-volume operations and optimizing storage space.
- Adoption of Electric and Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technologies: The shift towards sustainable energy sources presents a substantial opportunity for the forklift market. Electric forklifts, powered by lithium-ion batteries, offer reduced emissions and lower operating costs. Hydrogen fuel cell forklifts provide rapid refueling and consistent performance, even in refrigerated environments. As of 2024, approximately 50,000 hydrogen forklifts are in operation worldwide, predominantly in the U.S.
- Integration of Automation and Advanced Technologies: The incorporation of automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies into forklifts enhances operational efficiency and safety. Features such as obstacle detection systems, automatic braking, and proximity sensors reduce reliance on manual labor and align with the industry’s move towards smart manufacturing and logistics.
- Infrastructure Development in Emerging Markets: Developing countries are investing in infrastructure projects, including the construction of roads, ports, and industrial facilities. This development increases the demand for forklifts to handle materials and equipment, presenting growth opportunities in these regions.
- Emphasis on Workplace Safety and Ergonomics: There is a growing focus on enhancing workplace safety and operator comfort. Forklifts equipped with advanced safety features and ergonomic designs are in demand, as companies aim to reduce accidents and improve productivity.
Key Player Analysis
- Toyota Material Handling, Inc.: A division of Toyota Industries Corporation, Toyota Material Handling is a global leader in forklift manufacturing. In the fiscal year 2021/2022, the company reported net sales of approximately €20.83 billion, reflecting its dominant market position.
- KION Group AG: Headquartered in Germany, KION Group is the world’s second-largest forklift manufacturer. In 2023, the company generated revenues of €11.43 billion, underscoring its significant role in the material handling equipment sector.
- Mitsubishi Logisnext Co., Ltd.: This Japanese company is a prominent player in the forklift industry. In the fiscal year 2021/2022, Mitsubishi Logisnext achieved net sales of approximately €3.58 billion, highlighting its substantial market presence.
- Crown Equipment Corporation: Based in the United States, Crown Equipment is a leading manufacturer of electric forklifts and material handling equipment. In 2021, the company reported revenues of $4.1 billion, reflecting its strong position in the North American market.
- Anhui Heli Co., Ltd.: As China’s largest forklift manufacturer, Anhui Heli has a significant market share in the Asia-Pacific region. In 2021, the company reported revenues of $2.41 billion, indicating its growing influence in the global forklift market.
Recent Developments
- In May 9, 2023, Toyota Material Handling (TMH) introduced three innovative electric forklift models: the Side-Entry End Rider, Center Rider Stacker, and Industrial Tow Tractor. These additions enhance operational efficiency and versatility while ensuring top-tier performance and operator comfort.
- In September 26, 2023, The KION Group partnered with Li-Cycle Holding Corp. to recycle lithium-ion batteries at the Magdeburg, Germany plant. By 2030, the initiative aims to process up to 5,000 tonnes of battery material, supporting sustainable practices in forklift battery recycling.
- In 2024, Walmart allocated $200 million to autonomous forklift technology as part of its warehouse automation strategy. Initial deployment includes 19 FoxBots across four facilities, setting the stage for widespread integration based on performance reviews.
- In February 28, 2024, KION North America launched the Linde Series 1293 electric counterbalance forklifts, featuring 4,000–5,000 lb. capacities and Linde Li-ION batteries. These models balance sustainability with energy efficiency, helping businesses transition to greener operations.
Conclusion
The global forklift market is poised for substantial growth, driven by the rapid expansion of e-commerce, increased industrialization, and a shift towards sustainable material handling solutions. The adoption of electric and hydrogen fuel cell technologies is transforming operations, offering enhanced efficiency and reduced environmental impact. Advancements in automation and integration of smart technologies are further optimizing warehouse and logistics processes. However, challenges such as high initial investment costs, workforce safety concerns, and compliance with environmental regulations persist. Addressing these issues through innovation and strategic planning will be crucial for stakeholders aiming to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this evolving market landscape.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





