Table of Contents
Overview
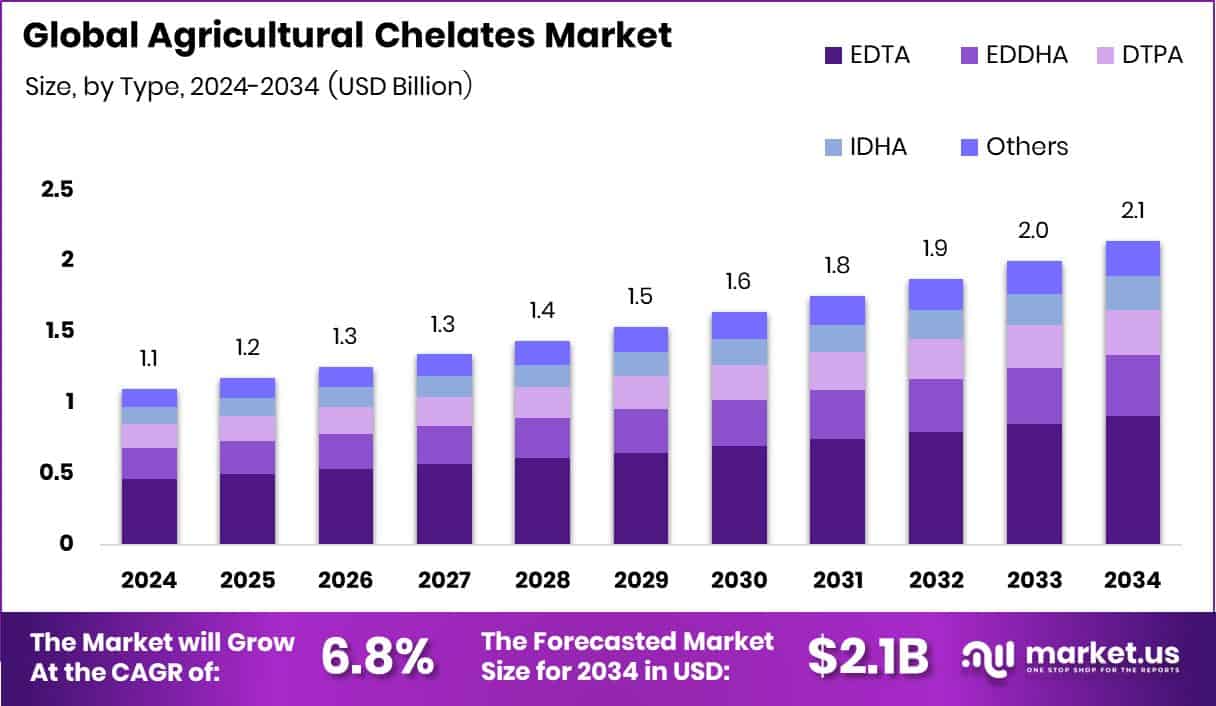
New York, NY – October 31, 2025 – The Agricultural Chelates Market, valued at USD 1.1 billion in 2024, is projected to reach USD 2.1 billion by 2034, growing at a 6.9% CAGR. Asia Pacific leads the market with a 43.40% share (USD 0.4 billion).
Agricultural chelates help crops absorb vital nutrients like iron, zinc, and manganese by preventing them from binding with soil particles, thereby improving soil fertility and yields. Global efforts to boost sustainable agriculture are accelerating this growth. The National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) invested $7.9 million to enhance soil health, while the FAO received $10 million from the USA for soil fertility mapping.
Rising soil degradation and micronutrient deficiencies are driving farmers toward chelate-based nutrient solutions. New ventures such as Uni Seoul, which raised Rs 5 crore, and Oncare, securing $1 million to establish ten production units, show growing investor confidence.
Strategic collaborations like Pivot Bio & Hefty Seed Co. and Sound Agriculture, which attracted $25 million in funding, highlight the sector’s innovation drive. Together, these initiatives are strengthening global food security and promoting sustainable, nutrient-efficient farming systems focused on long-term soil health and productivity.
➤ Click the sample report link for complete industry insights: https://market.us/report/global-agricultural-chelates-market/request-sample/
Key Takeaways
- The Global Agricultural Chelates Market is expected to be worth around USD 2.1 billion by 2034, up from USD 1.1 billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.9% from 2025 to 2034.
- EDTA type holds 42.4% share, showing its strong preference in chelate formulations globally.
- Soil application dominates with 38.2%, highlighting farmers’ trust in direct nutrient delivery methods.
- Iron chelates lead at 66.1%, proving their essential role in addressing crop deficiencies.
- Cereals and grains represent 38.6%, reflecting high adoption in staple food production worldwide.
- Agriculture accounts for 89.9%, making chelates a core tool for enhancing sustainable farming practices.
- The Asia Pacific Agricultural Chelates Market dominated with a 43.40% share, reaching USD 0.4 Bn.
➤ Directly purchase a copy of the report – https://market.us/purchase-report/?report_id=159625
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2024) | USD 1.1 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 2.1 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 6.9% |
| Segments Covered | By Type (EDTA, EDDHA, DTPA, IDHA, Others), By Mode of Application (Soil Application, Seed Dressing, Foliar Sprays, Fertigation, Others), By Micronutrient Type (Iron, Manganese, Others), By Crop Type (Cereals and Grains, Oilseeds and Pulses, Fruits and Vegetables, Others), By End Use (Agriculture, Indoor Farming) |
| Competitive Landscape | BASF SE, Nouryon, Dow, Yara International, ICL, Haifa Chemicals Ltd., Syngenta, Nufarm Ltd., Aries Agro Ltd., The Andersons, Inc. |
Key Market Segments
By Type Analysis
In 2024, EDTA dominated the By Type segment of the Agricultural Chelates Market, capturing a 42.4% share. Its leadership stems from its proven efficiency in chelating key micronutrients like iron, zinc, and manganese, enhancing their uptake by plants.
Farmers and agronomists favor EDTA for its cost-effectiveness and strong compatibility across various soil conditions, making it a dependable solution for boosting crop performance.
By improving nutrient solubility and preventing micronutrient deficiencies, EDTA supports higher yields and healthier soils. This dominant market share underscores its pivotal role in sustaining global agricultural productivity and promoting nutrient-efficient farming practices.
By Mode of Application Analysis
In 2024, Soil Application dominated the By Mode of Application segment of the Agricultural Chelates Market, accounting for a 38.2% share. This approach remains preferred due to its direct delivery of essential micronutrients to plant roots, promoting effective absorption and healthy crop development.
Farmers favor soil application for its compatibility with irrigation systems and ease of integration into traditional farming practices. It efficiently corrects nutrient deficiencies across diverse soils and crop types while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Its widespread adoption underscores its reliability in improving soil fertility and long-term productivity. Holding the largest share, soil application continues to stand as the most practical and trusted method for enhancing nutrient availability and sustaining agricultural growth worldwide.
By Micronutrient Type Analysis
In 2024, Iron dominated the By Micronutrient Type segment of the Agricultural Chelates Market, capturing a significant 66.1% share. This dominance reflects its critical role in addressing chlorosis and enhancing photosynthesis, especially in iron-deficient soils.
Iron chelates are widely used across major crops such as cereals, fruits, and vegetables, ensuring improved yields and superior crop quality. Farmers consistently rely on iron chelates due to their high efficiency in nutrient absorption and ability to strengthen plant vigor across diverse soil conditions.
Their proven performance and broad agricultural applicability make iron chelates the most trusted and extensively used micronutrient solution, firmly positioning them as a vital component in sustainable crop nutrition and soil health management.
By Crop Type Analysis
In 2024, Cereals and Grains led the By Crop Type segment of the Agricultural Chelates Market, commanding a 38.6% share. This leadership underscores the essential role of chelates in enhancing nutrient absorption for key staple crops such as wheat, rice, and corn, which are vital for global food security.
Chelate application in these crops boosts root growth, chlorophyll formation, and nutrient efficiency, resulting in improved yields and crop quality. As cereals and grains are cultivated on a large scale worldwide, farmers increasingly rely on chelates to sustain productivity and preserve soil fertility.
Their consistent effectiveness in maintaining balanced nutrition and supporting high-output agriculture has positioned cereals and grains as the most dominant and indispensable segment within the agricultural chelates market.
By End Use Analysis
In 2024, Agriculture dominated the By End-Use segment of the Agricultural Chelates Market, holding a substantial 89.9% share. This dominance reflects the sector’s strong dependence on chelates to overcome soil nutrient deficiencies and enhance crop productivity.
Chelates enable the efficient delivery of vital micronutrients such as iron and zinc, which are essential for robust plant growth and improved yields. Their adoption across a wide range of farming systems highlights their effectiveness in maintaining soil fertility and promoting sustainable cultivation.
With such an overwhelming market share, agriculture continues to be the primary driver of demand, reinforcing its pivotal role in advancing global food production and shaping the long-term expansion of the agricultural chelates market.
Regional Analysis
The Agricultural Chelates Market exhibits distinct regional growth trends shaped by varying soil conditions and farming systems. North America experiences steady expansion due to advanced agricultural technologies and growing awareness of soil nutrition management.
Europe follows with strong adoption driven by strict soil health regulations and the shift toward eco-friendly inputs. Asia Pacific leads the market, commanding a 43.40% share valued at USD 0.4 billion in 2024, supported by extensive cereal and grain cultivation and increasing efforts to combat soil deficiencies.
The Middle East & Africa show rising demand for nutrient-efficient solutions to improve productivity in arid conditions, while Latin America consistently contributes with its broad crop base and focus on yield optimization. Overall, Asia Pacific remains the key growth engine, setting the global direction for sustainable, nutrient-driven agricultural advancements.
Top Use Cases
- Correcting iron deficiency (chlorosis) in alkaline soils: In high-pH soils where iron becomes unavailable, using chelated iron helps plants absorb it. For example, as noted, when soil pH rises above 6.5, the least stable chelate (EDTA) may not work well, whereas more stable chelates like EDDHA remain effective up to pH 10.
- Delivering zinc more efficiently than conventional salts: Studies found that a chelated zinc form (Zn-EDTA) in wheat leaves was at least 2× as available compared to zinc sulfate in some soils, although it costs 5-10× more.
- Foliar or soil application of micro-nutrients under difficult soil conditions: When soils are deficient in micronutrients or have pH issues, chelated micronutrient fertilizers (such as for Fe, Zn, Mn) give better uptake and less risk of fixation in the soil.
- Integration with irrigation and fertigation systems: Many chelated fertilizers are water-soluble granules or liquids designed to be used with drip irrigation or foliar spray, enabling lower application rates. For example, one product description says they are easy to use with drip irrigation and are contained in chelated or EDTA form.
- Improving crop yield and quality via better nutrient availability: Chelated micronutrients deliver essential metals (like iron, manganese, and zinc) that plants need for key processes like photosynthesis, resulting in higher productivity and improved quality.
- Enabling micronutrient use in high-pH or otherwise unfavorable soils: For soils with poor micronutrient availability (e.g., alkaline, calcareous soils), chelates help prevent nutrients from getting locked up, thereby supporting plant growth more reliably.
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Dow completed the sale of its soil-fumigation product line “Telone™” for USD 121 million to TriCal Soil Solutions, Inc..
- In November 2024, Nouryon opened a new Innovation Center and expanded its office in Mumbai, India. The facility is geared to support major end-markets, including agriculture, where the company works on formulations like seed coatings, chelating agents, and crop-nutrition solutions.
- In July 2024, BASF announced plans to cease production of the active herbicide ingredient glufosinate-ammonium at its Knapsack and Frankfurt sites in Germany by the end of 2024 (with formulations to end in 2025) due to competitive and cost pressures.
Conclusion
The Agricultural Chelates Market is evolving as farmers focus on improving soil fertility and nutrient efficiency. Chelates play a key role in enhancing plant growth by ensuring vital micronutrients remain available for absorption, even in challenging soil conditions. Growing awareness about sustainable farming and environmental care is further supporting their use across global agricultural systems.
With advancements in formulation technologies and eco-friendly chelating agents, these solutions are helping farmers achieve higher yields while maintaining soil health. The market continues to move toward innovation and sustainability, shaping the future of modern, nutrient-balanced agriculture worldwide.
Discuss your needs with our analyst
Please share your requirements with more details so our analyst can check if they can solve your problem(s)





